Difference between revisions of "Military: Ariana"
(Tag: Visual edit) |
(Removed unnecessary bold and italics) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Military Forces == | == Military Forces == | ||
| − | Ariana’s military maintains a robust ground force with a smaller, agile air and sea force capability. The latest intelligence assessments indicate Ariana’s military has largely tier 2 capabilities with four separate Army Divisions with tier 1 capabilities. The tier two military forces consist of modern competitive military systems from two decades ago, fielded in significant numbers across the military’s force structure. Ariana recently upgraded equipment and weapon systems to attain selected tier 1 niche capabilities for certain divisional units including the following: 91st Tank, | + | Ariana’s military maintains a robust ground force with a smaller, agile air and sea force capability. The latest intelligence assessments indicate Ariana’s military has largely tier 2 capabilities with four separate Army Divisions with tier 1 capabilities. The tier two military forces consist of modern competitive military systems from two decades ago, fielded in significant numbers across the military’s force structure. Ariana recently upgraded equipment and weapon systems to attain selected tier 1 niche capabilities for certain divisional units including the following: 91st Tank, 92nd Motorized Infantry, 99th Special Purpose Forces (SPF), and 96th Airborne (ABN) Infantry. These tier 1 divisional units reflect a major military force with fielded state-of-the-art technology. |
Ariana’s forces field equipment to operate in all terrain with the ability to successfully conduct day and night operations. Ariana’s military also maintains links to regional criminal and terrorist groups that further extend the country’s potential as a global threat. (''For additional information on tier tables, see Section 4: Appendix C and the Worldwide Equipment Guide (WEG): Vol I, Chapter 1, OPFOR Tier Tables.'') | Ariana’s forces field equipment to operate in all terrain with the ability to successfully conduct day and night operations. Ariana’s military also maintains links to regional criminal and terrorist groups that further extend the country’s potential as a global threat. (''For additional information on tier tables, see Section 4: Appendix C and the Worldwide Equipment Guide (WEG): Vol I, Chapter 1, OPFOR Tier Tables.'') | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
Divisions and brigades are the Arianian army’s two largest tactical-level organizations. In peacetime, the army units are often subordinated to a larger, operational-level administrative command. The Arianian army might also maintain some separate, single-service, tactical-level commands (divisions, brigades, or battalions) directly under the control of their service headquarters. For example, major tactical-level commands of the air force, navy, strategic forces, and the SPF Command often remain under the direct control of their respective service component headquarters. The army component headquarters may retain centralized control of certain elite ground force elements, including airborne units and army SPF. This permits flexibility in employing these relatively scarce assets in response to national-level requirements. For these tactical-level organizations (division and below), the organizational directories contain standard table of organization and equipment (TO&E) structures. These administrative groupings normally differ from Ariana’s go-to-war (fighting) force structure. (''See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 3, Offense.'') | Divisions and brigades are the Arianian army’s two largest tactical-level organizations. In peacetime, the army units are often subordinated to a larger, operational-level administrative command. The Arianian army might also maintain some separate, single-service, tactical-level commands (divisions, brigades, or battalions) directly under the control of their service headquarters. For example, major tactical-level commands of the air force, navy, strategic forces, and the SPF Command often remain under the direct control of their respective service component headquarters. The army component headquarters may retain centralized control of certain elite ground force elements, including airborne units and army SPF. This permits flexibility in employing these relatively scarce assets in response to national-level requirements. For these tactical-level organizations (division and below), the organizational directories contain standard table of organization and equipment (TO&E) structures. These administrative groupings normally differ from Ariana’s go-to-war (fighting) force structure. (''See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 3, Offense.'') | ||
| − | Ariana fields | + | Ariana fields 15 divisions, Ariana’s largest tactical unit. Divisions can serve as the foundation to form DTGs, though that is not always the case. A division can fight as part of an OSC, an organization in the AFS (such as army or military region), or a separate unit in an FG. |
==== Army Doctrine and Tactics ==== | ==== Army Doctrine and Tactics ==== | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
=== Naval Forces Overview === | === Naval Forces Overview === | ||
| − | The Arianian navy patrols the Persian Gulf and maintains a small, agile contingent on the Caspian Sea. The navy has attempted to upgrade its capabilities with the purchase of Donovian ships | + | The Arianian navy patrols the Persian Gulf and maintains a small, agile contingent on the Caspian Sea. The navy has attempted to upgrade its capabilities with the purchase of Donovian ships and equipment, including submarines, missiles, and fast attack craft. Recently, the Arianian navy conducted exercises in the Persian Gulf that demonstrated at least a tier 2 rating for both equipment and training. |
Ariana maintains the strongest regional naval force after Donovia, and only the US Navy possesses enough ships and firepower to open the Strait of Hormuz if Ariana attempted to close it. If Ariana blocked shipment lanes in the Strait of Hormuz, many Middle Eastern countries would become essentially landlocked. | Ariana maintains the strongest regional naval force after Donovia, and only the US Navy possesses enough ships and firepower to open the Strait of Hormuz if Ariana attempted to close it. If Ariana blocked shipment lanes in the Strait of Hormuz, many Middle Eastern countries would become essentially landlocked. | ||
Revision as of 20:08, 1 August 2017
This page is a section of Ariana.
Ariana has an extensive history of various types of operations, from sponsorship of proxy terrorism to sustained force-on-force conflict. This history forms the basis for the military leadership mindset. The legacy of changing political boundaries between Ariana and its neighbors over the last century never terminated satisfactorily for the countries’ ethnic groups, familial-clan geographical demographics, or theological divisions.
Contents
- 1 Military Forces
- 2 Military Strategy
- 3 National Strategic Goals
- 4 Military Forces Overview
- 5 Military Functions
- 6 Research and Development Goals
- 7 Summary
Military Forces
Ariana’s military maintains a robust ground force with a smaller, agile air and sea force capability. The latest intelligence assessments indicate Ariana’s military has largely tier 2 capabilities with four separate Army Divisions with tier 1 capabilities. The tier two military forces consist of modern competitive military systems from two decades ago, fielded in significant numbers across the military’s force structure. Ariana recently upgraded equipment and weapon systems to attain selected tier 1 niche capabilities for certain divisional units including the following: 91st Tank, 92nd Motorized Infantry, 99th Special Purpose Forces (SPF), and 96th Airborne (ABN) Infantry. These tier 1 divisional units reflect a major military force with fielded state-of-the-art technology.
Ariana’s forces field equipment to operate in all terrain with the ability to successfully conduct day and night operations. Ariana’s military also maintains links to regional criminal and terrorist groups that further extend the country’s potential as a global threat. (For additional information on tier tables, see Section 4: Appendix C and the Worldwide Equipment Guide (WEG): Vol I, Chapter 1, OPFOR Tier Tables.)
Military Strategy
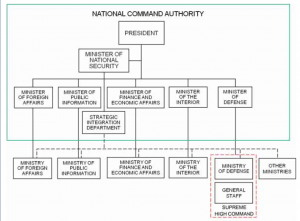
National Command Authority
All countries share a similar National Command Authority (NCA) construct including Gorgas, who refers to it as a National Council. The Ariana NCA exercises overall control over the application of all national power instruments to plan and carry out the country’s national security strategy. The NCA includes cabinet ministers responsible for military and civilian instruments of power such as the Ministers of Foreign Affairs, Public Information, Finance and Economic Affairs, Interior, and Defense. The Arianian president chairs the NCA and may select additional members.
The president appoints the Minister of National Security, who is responsible for the NCA’s Strategic Integration Department (SID). The SID is the overarching agency responsible for integrating all national power instruments under one cohesive national security strategy. The SID coordinates the plans and actions of all Ariana’s ministries, but particularly those associated with the national power instruments. (See TC 7-100.2 Opposing Force Tactics: Chapter 1, Strategic and Operational Framework.)
Strategic Operational Framework
The strategic operational framework for all countries in the Caucasus region is similar in construct and application, primarily the result of historic influences. The NCAs and the NC for all five countries exercise command and control (C2) of the Armed Forces via the Supreme High Command (SHC), which includes the Ministry of Defense (MOD) and a General Staff drawn from all the service components. In peacetime, the MOD and General Staff operate closely but separately. The MOD assumes responsibility for policy, acquisitions, and financing the Armed Forces. The General Staff promulgates policy and supervises the service components while its functional directorates are responsible for key aspects of defense planning. In wartime, the MOD and General Staff merge to form the SHC, which functions as a unified headquarters.
All five countries currently configure their militaries using an administrative force structure (AFS) for managing military forces in peacetime. This administrative force contains the aggregate of various military headquarters, facilities, and installations designed to man, train, and equip the forces. In peacetime, the various militaries group their forces into corps and armies for administrative purposes. In some cases, the militaries may group their forces administratively under geographical commands designated as military regions or military districts. If the SHC elects to create more than one theater headquarters, it may allocate parts of the administrative force structure to each of the theaters, normally along geographic lines. Typically, these administrative groupings differ from the country’s go-to-war (fighting) force structure. Other parts of the administrative force structure consist of assets centrally controlled at the national level. (See FM 7-100.4 Opposing Force Organization Guide: Chapter 3, Task Organizing.)
National Strategic Goals
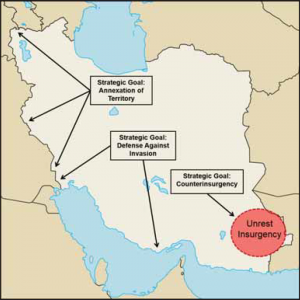
The Arianian military has four priorities based upon the country’s history. First, it wants to become the dominant regional military power. Second, the Arianian military must be strong enough to defend its borders, control the Strait of Hormuz, and deny access to hostile powers. Third, Ariana remains focused on maintaining weapons of mass destruction because some Arianians believe such weapons will deter conventional aggression by enemies and are the rightful possession of a great power, as Ariana views itself. This explains Arianian efforts to continue enhancing the country’s nuclear capability. Ariana’s final priority is global deployment of smaller clandestine units (irregular forces) to train and equip other anti-Western factions. This focus has two advantages for the Arianians, as it both disrupts US interests and creates an outlet for weapons sold by the Arianian military complex.
The NCA determines the direction and scope of Ariana’s strategic mission. Ariana’s overall goals are to continually expand its dominance within the region and eventually change its position within the global community. These long-term aims are supported by one or more specific goals, each based on a particular threat or opportunity, including:
- Defense of Ariana’s sovereignty
- Economic expansion
- Destruction of insurgent groups
- Acquisition of natural resources located outside Ariana’s borders
- Preclusion or elimination of outside intervention
Implementing National Security Goals
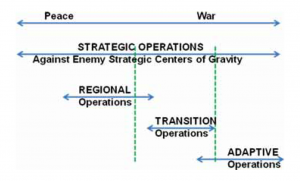
All five countries share similar strategies to achieve their national goals. Strategic operations for all five countries remain a continuous process not limited to wartime or war preparation. Once war begins, strategic operations continue during regional, transition, and adaptive operations and complement those operations. Each of the latter three types of operations occurs only during war and only under certain conditions. Transition operations can overlap regional and adaptive operations.
In pursuit of their national security strategies, all five countries are prepared to conduct four basic types of strategic-level courses of action:
- Strategic operations use all instruments of power in peace and war to achieve a country’s national security strategy goals through attacks against the enemy’s strategic centers of gravity.
- Regional operations include conventional, force-on-force military operations against overmatched opponents, such as regional adversaries and internal threats.
- Transition operations bridge the gap between regional and adaptive operations and contain some elements of both. The country continues to pursue its regional goals while dealing with developing outside intervention that has the potential to overmatch its military.
- Adaptive operations preserve the country’s power and apply it in adaptive ways against opponents that overmatch the country’s military.
National Security Strategy
Although Donovia, Ariana, Atropia, Gorgas, and Limaria may refer to them as “operations,” each of these courses of action is actually a subcategory of strategy. Each type of operation aggregates the effects of tactical, operational, and strategic actions in conjunction with instruments of national power to achieve each country’s strategic goals. The types of operations employed at a given time will depend on the types of threats, opportunities, and other conditions present.
Each country’s strategy typically starts with actions directed at a regional opponent that the government overmatches in conventional military power, as well as other instruments of power. If possible, each government will attempt to achieve its ends without armed conflict. Accordingly, these governments do not limit strategic operations to military means and usually do not begin with armed conflict. They may achieve the desired goal through pressure applied by nonmilitary instruments of power, perhaps by merely threatening to use superior military power against the opponent. These actions fall under the general framework of “strategic operations.”
The government may resort to armed conflict to achieve its desired end state when nonmilitary means prove insufficient or not expedient. Strategic operations, however, continue even if a particular regional threat or opportunity causes the country to undertake “regional operations” that may include military means. Prior to the initiation of hostilities and throughout the course of armed conflict with its regional opponent, the government will continue to conduct strategic operations to preclude intervention by outside players, other regional neighbors, or an extra-regional power that could overmatch its forces. Such operations, however, always include branches and sequels to deal with the possibility of intervention by an extra-regional power.
Military Forces Overview
Military Strategy
Ariana conducts overt and covert operations in order to maintain its position within the region. The country maintains strong relationships with Limaria and has ties with Donovia. Ariana also is focused on keeping Western influence out of the region and maintaining its current status as a regional strongman.
Army Overview
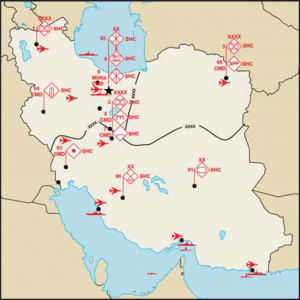
The Arianians maintain a robust ground force capability that consists of a conventional military capable of conducting a wide range of operations. Multiple sources indicate the ground forces, which include paramilitary groups that supplement the regular army, boast an estimated 790,600 troops. The ground forces consist of three mechanized armies.
The ground forces tend to deploy along the country’s external borders, particularly those with Iraq and Atropia, which are seen as the most likely land avenues for Western forces to approach. The military also tends to protect key infrastructure such as potential nuclear sites, dams, and political buildings.
Arianian ground forces will play the major role in any foreign invasion scenario. If a country invaded Ariana— most likely through the Persian Gulf or Iraq—the invader would face a wave of ground forces consisting of mechanized infantry. The ground forces would likely exert their main effort to repel the invader in a conventional force-on-force engagement.
A terrain analysis of Ariana’s physical environment quickly explains the disposition of its military forces. The Zagros Mountains channelize movement from the northwest to the southeast. Overall, Ariana’s size and terrain dictate the country’s defense strategy. When facing an extra-regional force, a possible course of action would be for the ground forces to fight a retrograde delay that would maximize the advantages of the difficult terrain to draw an invader into Ariana and extend its logistical lines. The Arianians could fight on interior lines of communication, a course of action that would allow them to concentrate on the enemy at choke points such as mountain passes.
Originally, the Arianian military developed mainly as a defensive force with the primary objective of maintaining territorial integrity. Some elements, however, received an additional mission to export ideology and policy abroad. While most unit leaders come from Ariana’s more educated classes, fundamentalists and religious zealots lead some units, receiving their positions as a result of their perceived loyalty to the regime rather than their qualifications. Recently, the Arianian military initiated a program to educate and professionalize the force no matter how the leaders obtained their current position.
Army Size and Structure
The maneuver brigade serves as Ariana’s basic combined arms unit. In the AFS, some maneuver brigades are constituent, or organic, to the base structure, such as divisions. The NCA calls them divisional brigades. These armies, however, organize some units as separate brigades, designed to possess greater ability to accomplish independent missions without further allocation of forces from a higher tactical-level headquarters. Separate brigades possess some subordinate units with the same force structure as a divisional brigade of the same type (for example, the headquarters); some units that are especially tailored to the needs of a separate brigade, marked “(Sep)” in the organizational directories; and some that are the same as units of this type found at division level, marked “(Div).”
The Arianian army designs its maneuver brigades to serve as the basis to form a brigade tactical group (BTG) if necessary. A brigade, separate or as part of a BTG, can fight as part of a division or division tactical group (DTG), a separate unit in an operational-strategic command (OSC), an organization of the AFS (such as army, corps, or military district), or as part of a field group (FG). (See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 2, Command and Control.)
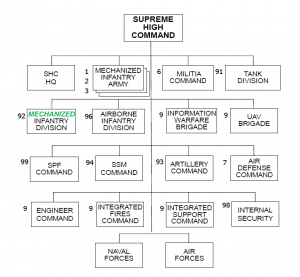
The Arianian ground forces consist of three (1st, 2nd, 3rd) mechanized infantry armies. Support and special purpose elements include air defense, artillery, engineer, militia, special purpose forces (SPF), and missile commands. Recently, Ariana established an Information Warfare (INFOWAR) brigade to develop electronic and computer warfare capabilities. (See diagram on page 2A-2-4 and the Order of Battle (OB) at the end of this country’s variable).
Divisions and brigades are the Arianian army’s two largest tactical-level organizations. In peacetime, the army units are often subordinated to a larger, operational-level administrative command. The Arianian army might also maintain some separate, single-service, tactical-level commands (divisions, brigades, or battalions) directly under the control of their service headquarters. For example, major tactical-level commands of the air force, navy, strategic forces, and the SPF Command often remain under the direct control of their respective service component headquarters. The army component headquarters may retain centralized control of certain elite ground force elements, including airborne units and army SPF. This permits flexibility in employing these relatively scarce assets in response to national-level requirements. For these tactical-level organizations (division and below), the organizational directories contain standard table of organization and equipment (TO&E) structures. These administrative groupings normally differ from Ariana’s go-to-war (fighting) force structure. (See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 3, Offense.)
Ariana fields 15 divisions, Ariana’s largest tactical unit. Divisions can serve as the foundation to form DTGs, though that is not always the case. A division can fight as part of an OSC, an organization in the AFS (such as army or military region), or a separate unit in an FG.
Army Doctrine and Tactics
The Arianian army derives most of its doctrine and tactics from Donovian military doctrine. The Arianian army gears its doctrine and tactics toward the opposition and the physical environment. Ariana can conduct large-scale operations, fluctuate back and forth from adaptive tactics, or operate in a hybrid configuration. Similar to most armies today, Arianian ground forces currently employ tactical control measures, including assembly areas, forming-up assembly areas just prior to attacks, advance axes, checkpoints, jump-off lines (similar to Western lines of departure), and attack lines. The Arianian military will likely engage, hoping to push back invaders or buy time to mobilize reserves and for adaptive doctrine to begin.
Army Training and Readiness
Ariana fields a well-trained army. Most units maintain a 98% operational readiness rate.
Army Equipment and Weapons
Ariana’s equipment and weapons largely reflect tier 2 capabilities with certain army divisions with tier 1 capabilities within the military’s force structure. The Arianian army recently upgraded some systems for selected tier 1 niche capabilities. The Arianian army has the equipment to operate in all terrain types and successfully conduct both day and night operations. (For further information see Section 4: Appendix C or the WEG: Vol. 1, Chapter 1, OPFOR Tier Tables.)
The Arianian navy patrols the Persian Gulf and maintains a small, agile contingent on the Caspian Sea. The navy has attempted to upgrade its capabilities with the purchase of Donovian ships and equipment, including submarines, missiles, and fast attack craft. Recently, the Arianian navy conducted exercises in the Persian Gulf that demonstrated at least a tier 2 rating for both equipment and training.
Ariana maintains the strongest regional naval force after Donovia, and only the US Navy possesses enough ships and firepower to open the Strait of Hormuz if Ariana attempted to close it. If Ariana blocked shipment lanes in the Strait of Hormuz, many Middle Eastern countries would become essentially landlocked.
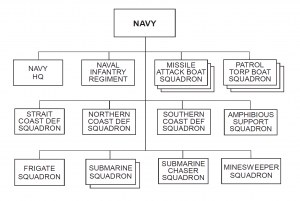
Like most navies, the Arianian navy’s shore establishment borders its sea frontiers. The Arianian navy divides the country into four naval districts. The First Naval District, also the most important, sits astride the Strait of Hormuz at Bandar-e Abbas. This is Ariana’s most modern and well- developed port facility and where Ariana constructed its main repair facilities. It also serves as the home port for most of its larger ships. The Second Naval District covers the northern Persian Gulf, and Third Naval operates in the general vicinity of the northern Persian Gulf. The Fourth Naval District covers Ariana’s northern border where it shares the Caspian Sea with Donovian and Atropian fleets.
Ariana also has an Indian Ocean base in the very southeastern part of the country near the Pakistan border. This base serves as the Arianian navy’s main outlet to the open sea. Some experts believe this port will eventually become the home port for the submarines currently berthed at Bandar-e Abbas. (See diagram on page 2A-2-10 and the OB at the end of this country’s variable).
Arianian naval strategy has four main priorities:
- Control the Strait of Hormuz and thereby access to the Persian Gulf
- Project naval power into the Persian Gulf and dominate the disputed islands there
- Disrupt sea lines of communication for nearby countries
- Intimidate other countries through its naval presence
Although Ariana maintains the second most capable regional naval force, it will likely operate more or less as a “guerilla navy.” The Arianian navy would employ small boats in hit-and-run type missions, deploy mines, fire anti-ship cruise missiles, and use fixed wing and helicopter forces against stronger naval forces.
Arianian naval missions might include:
- Mine laying, particularly of narrow channels and coastal areas
- Insertion/extraction of SOF
- Seizure of disputed islands
- Raids on coastal areas and isolated oil rig platforms
- Harassment and closure of the Strait of Hormuz
- Defensive patrolling of coastal areas
Ariana created a new and mixed naval dimension with the recent acquisition of three Donovian submarines currently based at Bandar-e Abbas. A foreign navy could bottle up the submarines because of the location of Bandar-e Abbas in the constricted Strait of Hormuz.
There are seven naval bases including one headquarters element in Ariana’s capital. The majority of the bases are in the Persian Gulf. The total service fleet consists of 120 craft and 24 submarines.
Ariana’s naval forces can successfully conduct day and night operations. Ariana’s navy is well- trained and at a high rate of readiness. Most naval units maintain operational readiness rates of approximately 93%.
Ariana’s naval equipment and weapons contain largely tier 2 capabilities throughout the navy’s force structure, which is based on modern competitive military systems fielded over the last 10 to 20 years. Upgrades to some systems, however, provide a number of tier 1 niche naval capabilities.
Air Force Overview
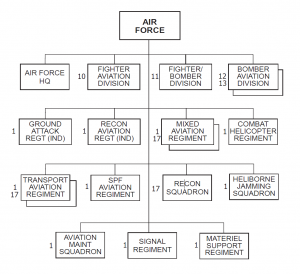
Ariana divides its air force into three commands: Western, Southern, and Eastern. The Arianian air force consists of four divisions, with the 10th Fighter Aviation Division as the premier air force unit.
The air force has a reputation for flying skill and the ability to put ordnance on target. Recent exercises provide evidence that, for regional standards, Arianian pilots remain skillful in air strikes against ground targets and using terrain to mask themselves from radar. Arianian pilots maintain a deep strike capability. The air force primarily supports its ground forces and is likely positioned near strategic sites such as nuclear plants, dams, and government buildings in order to intercept enemy air activity.
Air Force Size and Structure
The Arianian air force fields four aviation divisions divided up into one fighter, two bomber and one fighter/bomber units based on their aviation assets. It also possesses several other regiments designed for ground attack, reconnaissance, combat operations, transportation, or Arianian SPF unit support. The Arianian air force also has limited heliborne jamming capabilities. (See the OB at the end of this country’s variable).
Air Force Doctrine and Tactics
The Arianian air force modified its doctrine and tactics based on observing other countries’ conflicts, including the US. It will use force-on-force engagement with a regional competitor. Additionally, the Arianian air force will likely exhibit a show of force as a warning before actually committing to air combat and use its air force to support ground troops and protect key infrastructure.
Air Force Training and Readiness
Ariana’s air force operates mostly well-trained units with a 95% equipment operational readiness rate throughout.
Air Force Equipment and Weapons
The Arianian air force operates mainly tier 2 equipment and weapons, but now possesses limited modern upgrades and the potential for random tier 1 niche capabilities. Ariana’s air force can successfully conduct day and night operations. (For further information see the WEG, Vol 2: Airspace and Air Defense Systems.)
Government Paramilitary Forces
The Arianian government tasks its paramilitary forces (government forces like police that are distinct from regular armed forces yet similar in organization or training) with the following missions: basic law enforcement, border control, and maintenance of public order. Arianian agencies with these responsibilities include the Ministry of Intelligence and the Law Enforcement Forces under the Interior Ministry. Last year, the US State Department reported Ariana’s security forces and paramilitary forces faced corruption issues and acted with impunity as they conducted serious human rights violations, especially when reacting to demonstrations after recent presidential elections.
Non-State Paramilitary Forces
Insurgent/Guerrilla Forces
Attempting to generalize the irregular conflict motivation of different population segments is problematic. Nonetheless, two major considerations are an ethnocentric or separatist motivation compared to a nationalistic motivation. Such strife has devolved to forms of irregular warfare and a violent struggle among state and non-state actors to gain legitimacy and influence over relevant segments of the population.
Several foreign anti-Ariana insurgent groups operate with sporadic violence and have attacked current government entities and key leaders. The largest group is located in southeast Ariana and has been opposing leaders for two decades through a low-level pseudo-insurgency. The group, God’s Helpers Brigade, promotes violent populace opposition to state taxation policies; unreliable electrical service, sewage treatment, and potable water issues; substandard medical preventive services; lack of access to state education programs for working class citizens; and a state judicial system that illegally favors the political party currently in control of the executive and legislative branches of the government.
Other groups and affiliates across Ariana are sympathetic to pro-Western economic initiatives and social-political state governance concepts. Whether these groups align with a pro-Western coalition in future possible operations or continue with separate domestic agendas, the distinction between criminal organizations, private militia, insurgents, or guerrillas will be significant in assessing which forces support coalition objectives.
At least three forms of armed and unarmed combatants will emerge from these domestic groups if a regional host nation invites US and coalition presence to the area. First, factions may oppose the host nation government and be unfriendly toward the US-coalition presence. These factions will initiate overt resistance through violent and nonviolent protests against the host nation and US coalition. Next, factions will oppose host nation government policies but be potentially friendly toward the US coalition presence when this regional presence promotes and supports a domestic faction agenda. Third, several extremist factions will quickly resort to expanded terrorism if a US coalition enters the region. The groups will initially target US coalition forces, logistical staging points, host nation law enforcement, and internal security forces. Any of these domestic factions can be influenced by financing, training, and materiel support from foreign entities that are intent on agitating civil unrest or insurgency-like actions in the region.
Operational reach actions range from subversive and violent confrontations with adversary nation- states or a host nation government in power, to actions by a contracted individual or small cell capable of inflicting strategic consequences. Irregular forces can be unusually flexible and adaptable in ways and means to counter traditional advantages of stronger opponents, disregard sanctions intended to control conflict, and optimize actions with self-announced justification based on populist regional social justice or ideological perspectives. An irregular force will optimize a range of organizational options, from small, loosely affiliated cells to global networks, in order to promote mission success and psychological effect. Such networks can be local, regional, international, or transnational affiliations; host simple or sophisticated media affairs programs; and attain covert or overt financial, political, military, economic, or social support. In summary, people conducting irregular warfare will seek to gain capabilities such as co-opting an indigenous population or hiring a domestic criminal organization, encouraging a militia with robust international connections, protecting transnational networking affiliations, or applying a combination of these capabilities to degrade practical or perceived power by a rival criminal organization or militia, or the host nation governmental authority.
The NCA commands the militia, another category of reserve military personnel that was formed about 20 years ago. The militia became famous when young boys martyred themselves in suicidal human wave attacks against Iraq during the border wars. The militia can conduct limited traditional military operations; most units can perform civil support missions.
Criminal Organizations
Despite a lack of official reports on criminal enterprises, the country’s drug and weapons trades remain lucrative businesses. Reports indicate certain SPF elements have links to the black market. These domestic elements generally are categorized with criminal organizations.
Private Security Organizations
In troubled areas of Ariana, small groups of local civilians band together to provide security for their businesses, homes, and families, as these people feel that the police and military cannot arrive in time when trouble does occur. The news media indiscriminately uses the “militia” label when reporting armed violence in the region by such groups. A militia is commonly defined as a paramilitary force organized and controlled by a sovereign government similar to an internal security force. Although militias typically are not irregular forces, some groups of armed Arianian individuals band together formally or informally, and either self-declare or are categorized with the “militia” term.
Nonmilitary Armed Combatants
While nonmilitary armed combatants (insurgent forces, guerrilla forces, criminal organizations, and private security organizations) may not see eye-to-eye with the Arianian government, they are at best neutral in support of US activities in the region and at worst, predominately hostile.
Military Functions
Command and Control
The core of Ariana’s command and control (C2) concept remains the assumption that modern communications are susceptible to attack and/or monitoring. Accordingly, the military operates from the view that centralized planning helps assure both command (establishing the aim) and control (sustaining the aim), leading to strategic and operational directions. Necessarily then, the military relies on the loyalty of its forces and extends far-ranging authority for troops to act while foregoing rigorous control as unproductive in the modern environment. (See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 2, Command and Control.)
Arianian military battalions have a headquarters composed of a command section including the commander, deputy commander, and a small staff element, as well as a staff section with the chief of staff and the remainder of the battalion staff. The battalion staff consists of the operations officer, assistant operations officer, intelligence officer, and resources officer. The signal platoon leader also serves as the battalion communications officer, and the reconnaissance platoon leader acts as the chief of reconnaissance, while the materiel support platoon leader serves as the battalion resources officer. (See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 2, Command and Control.)
C2 at the tactical level of command emphasizes survivability through mobility, redundancy, and security. Command posts and procedures are streamlined at the operational level, relying heavily on common procedures for important recurring tactical tasks.
Maneuver
The Arianian military has a robust capability to conduct combined arms operations; the basic combined arms unit is the maneuver brigade. In the administrative force structure, maneuver brigades are typically constituent to divisions—called divisional brigades. However, some are organized as separate brigades, designed to have greater ability to accomplish independent missions without further allocation of forces from higher-level tactical headquarters.
Air Defense
The Arianian Air Defense Command (ADC), subordinate to the Supreme High Command, provides air defense coverage for Arianian units. It also supports combined arms combat by the comprehensive integration of a large number and variety of weapons and associated equipment into an effective, redundant air defense system. Employment of this system pursues the basic objectives of air defense by employing certain concepts and principles. This is best accomplished by establishing an integrated air defense system (IADS). Air defense weapons and surveillance systems at all levels of command are part of an IADS. This ability provides a continuous, unbroken (usually overlapping) umbrella of air defense coverage and presents a significant threat to any potential enemy air activity.
Ariana recognizes that air defense is an all-arms effort. Thus, all ground units possess some type of an organic air defense capability to differing degrees, depending on the type and size of the unit. The ADC continuously looks for new and adaptive ways of employing not only air defense systems but also systems not traditionally associated with air defense. Many weapons not designed as air defense weapons will also damage and/or destroy tactical aircraft when within range.
Throughout maneuver units, there are a number of systems designed for air defense and other systems that can be used in an air defense role. The heavy antiaircraft machineguns on tanks are specifically designed for air defense. Machine guns on armored personnel carriers and automatic cannon on infantry fighting vehicles can engage both ground and air targets. Most antitank guided missiles (ATGMs) are extremely effective against low-flying helicopters. Several ATGM manufacturers offer antihelicopter missiles and compatible fire control, which are especially effective against low-flying rotary-wing aircraft. Field artillery and small arms can also be integral parts of the air defense scheme. All these weapons can be extremely lethal when used in this role.
Ariana considers every soldier with a man-portable air defense system (MANPADS) to be an air defense firing unit. These weapons are readily available at a relatively low cost and are widely proliferated. Therefore, Arianian ground forces are acquiring as many MANPADS as possible and issuing them in large numbers to a wide variety of units. The military can also disseminate them to selected affiliated forces. The small size and easy portability of these systems provides the opportunity for ambush of enemy airframes operating in any area near Arianian units. Ground units also employ them to set ambushes for enemy helicopters, especially those on routine logistics missions. (For more information, see TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 11, Air Defense.)
INFOWAR
Ariana defines information warfare (INFOWAR) as specifically planned and integrated actions to achieve an information advantage at critical points and times. The goal is to influence an enemy’s decision-making cycle through collected and available information, information systems, and information-based processes, while retaining the ability to employ friendly information and information-based processes and systems. Ariana has a robust INFOWAR capability with the brigade headquarters out of Tehran.
RISTA
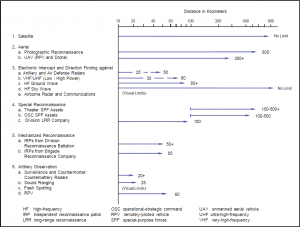
Reconnaissance, intelligence, surveillance, and target acquisition (RISTA) is viewed as the single- most important function for the Arianian military. Thus, Arianian forces typically commit significant resources to RISTA-related operations, which are usually aggressive with overlapping redundancy in the intelligence disciplines. The table on the next page summarizes the effective ranges for reconnaissance assets that can support Ariana’s tactical commanders.
Fire Support
Arianian military doctrine stresses that fire support combines air assets, surface-to-surface missiles, and artillery into an integrated attack against enemy defenses as well as for offense operations. In past conflicts, Ariana’s military successfully integrated fire support into operations, from close to deep-strike capability. The commanders always seek to increase the effectiveness of air and missile strikes and artillery fire to destroy enemy formations, weapons systems, or key components of an enemy combat system. (See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 9, Indirect Fire Support.)
Protection
Ariana will attempt to minimize civilian casualties to a large extent. The military has engineering assets to reinforce civilian and military positions. The C2 and fire support systems are sophisticated enough to minimize the threat of “friendly fire” or other accidents. However, military and civilian populations are closely integrated, making it difficult for invaders to launch attacks without the risk of civilian casualties that would enrage the population and be used as ammunition for INFOWAR. (See TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 12, Engineer Support and Chapter 7, Information Warfare.)
Logistics
The Arianian military fields a robust logistics capability that can support its maneuver units for any length of time. Ariana’s military continues to improve its logistics systems, including increased emphasis on support zone security and plans to stockpile war materiel throughout the country.
Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear
Ariana possesses a capable and growing chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) capability. In this region emerging CBRN capability and technology is viewed as a status symbol. Countries possessing these capabilities are firm in their belief that they should be viewed as a powerbroker and that their weapons equate to symbols of national might with the ability to have regional and possibly strategic impact.
Arianian strategic policy supports a CBRN first strike in the event it believes its national security is in jeopardy. National policy also supports the use of preemptive CBRN strikes against a neighbor either to deter aggression or as a response to an enemy attack. It may also use, or threaten to use, CBRN weapons as a way of applying political, economic, or psychological pressure.
Ariana has a wide variety of CBRN delivery means organic to its military forces. In addition to surface-to-surface missiles capable of carrying CBRN warheads, most Arianian artillery systems are capable of delivering chemical munitions. Artillery systems that are 152-mm or larger are also capable of firing nuclear rounds. The Arianian air force can also use its aircraft to deliver a CBRN attack. Trained Arianian SPF may also be used as alternate means of delivering CBRN munitions packages. Ariana is also well-prepared to employ civilian and military CBRN protection measures and has chemical defense units organic to all division and brigade maneuver units.
Ariana has a substantial industrial base that produces large quantities of toxic industrial chemicals (TIC), which are chemical substances possessing acute toxicity. An adjunct to chemical weapons is use of TIC, which can easily be exploited as improvised (or converted into) chemical weapons by military and civilians alike. (For a listing of possible high- and moderate-risk TIC possibly available to Ariana see the WEG, Vol. I, Chapter 14, Improvised Military Systems.)
For additional information on the capabilities, release authority (NCA), and employment of CBRN see TC 7-100.2: Opposing Force Tactics, Chapter 13, CBRN and Smoke. For specific technical information, delivery means, agents, and effects of CBRN see the WEG, Vol. I, Chapter 11, Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear (CBRN).
Research and Development Goals
Over the past two decades, Ariana carried out secretive research supporting its uranium enrichment program, which directly violated the policy set forth by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). During this time period, Ariana strongly refuted any claims that it sought nuclear weapons while covertly pursuing a dual parallel uranium enrichment program. One program uses a laser process (based on Donovian technology) and the other applies a centrifuge process. The Donovian government terminated cooperation with Ariana on the laser enrichment program after extensive dialogue with the US, and the program still appears inactive. Ariana admitted that it has obtained uranium centrifuge technology through unofficial channels. Recently, Ariana became the tenth country in the world to develop a nuclear weapon. Though less powerful in terms of kilowatts compared with other nuclear powers, Ariana now possesses a small number of tactical nuclear weapons.
Summary
Ariana maintains the second-strongest military in the region after Donovia, with primarily tier 1 and 2 equipment. Ariana operates a capable army, navy, and air force that provide it with a considerable edge compared to its neighboring countries. The Ariana military has the capability to inflict severe losses on any military force that attempts to invade its homeland, but also fields the forces to conduct offensive operations against neighboring countries.