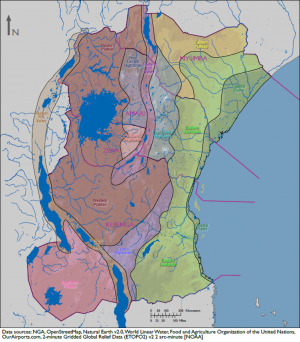
Physical Environment: Ziwa
Ziwa is a relatively small country located in central Africa. It is a completely landlocked country that encompasses a portion of Lake Victoria, Lake Natron, and Lake Eyasi. The country’s terrain varies from significant a rift valley and lakes in East. Arid desert lowlands and open savannah comprise a majority of the country. Climates range from semiarid and in the west, warm desert and arid climate with increased humidity near Lake Victoria.
Contents
Table of Physical Environment Data
| Measure | Data | Remarks |
| Total Area (sq. miles) | 43,116 | Includes inland water |
| Land Area (sq. miles) | 34,216 | Excludes inland water |
| Inland Water (sq. miles) | 8,900 | Includes Lake Victoria |
| Inland Border (miles) | 924 | Amari (437), Kujunga (437) |
| Coastline (miles) | 884 | Lake Victoria (884) |
| Highest Elevation (ft.) | 10,613 | Jaeger Summit |
| Lowest Elevation (ft.) | 1,913 | Lake Natron |
| Arable (cultivated) Land (%) | ||
| Permanent Crops (%) | ||
| Permanent Pasture (%) | ||
| Irrigated Land (%) | ||
| Forested Land (%) | ||
| Urban Area (%) |
Terrain
Most of Ziwa sits at the center of the East Africa's Western Plateau, which is mostly savanna extending south of Lake Victoria. The Eastern Highlands make up Ziwa's eastern border with Amari and is home to the Olduvai Gorge and Ngorogoro Crater, historical anthropological and wildlife sites. The border lakes, Eyasi and Natron, form the southern portion of East Africa's Eastern Rift Valley, extending northward through Amari and into Nyumba's Lake Turkana.
Border Disputes
Ziwa is on good terms with both Amari and Kujenga with respect to border agreements. However, the southern and western borders with Kujenga are extremely remote and rarely patrolled by either country.
Bodies of Water
Lake Victoria comprises the northwest corner of Ziwa which it shares with Amari and Kujenga. It is the largest tropical freshwater lake in the world. Over half a million Ziwans live on the lake's large islands. Lakes Eyasi and Natron, by contrast, are shallow salt-water lakes with extreme seasonal variance in water levels. No significant rivers flow through Ziwa. The Mbalangeti River flows from the Eastern Highlands into Lake Victoria's Speke Gulf, 100 km northeast of Mwanza. Even smaller rivers flow into Ziwa's two other gulfs on the southern shore Lake Victoria. Major wetlands and swamps characterize all of these river-lake boundary zones.
Mobility Classification
Since most of Ziwa sits on the fairly accessible Western Plateau, the main factor on mobility would be road quality rather than terrain for the majority of the country.
Movement in Ziwa is most restricted along the Eastern Rift Valley and Eastern Highlands. Steep escarpments separate the two Rift Valleys from their surrounding terrain; both valleys contain active volcanoes. Mountainous terrain and rough roads make it hard to transport troops and equipment overland. Rivers, streams, and wetlands also challenge mechanized and motorized movement in this region. Roads can become flooded during the rainy season, making them impassable. These rains also greatly affect visibility for reconnaissance and air operations. Foot movement is also limited in the Eastern Highlands by the negative effects of the high altitudes.
Natural Hazards
Both natural disasters and manmade hazards exist in Ziwa. Natural disasters include flooding, earthquakes, limited volcanic activity in the Rift Valleys, landslides, windstorms, and hailstorms. Frequent droughts can lead to famine. Violent thunderstorms with gusty winds are common on and around Lake Victoria. Water pollution is an issue, caused by urban waste, industrial waste, and contamination by pesticides and fertilizer. Dangerous wildlife include disease-carrying mosquitoes and tsetse flies, as well as more traditional threats from African big game animals.
Subterranean Environment
Negligible. Though Ziwa has many gold and gem mines, these are mostly open pits.
Vegetation
The Western Plateau is mostly open savanna and grassland. Ziwa's densest vegetation is along the southern shores and islands of Lake Victoria and in small deciduous forests in the Eastern Highlands.
Agriculture
Ziwan farmland is almost entirely irrigated by rainfall and cultivated by subsistence farmers. Crops on the Western Plateau are cassava and other root vegetables. A small but growing aquaculture industry is developing along the southern shore of Lake Victoria.
Livestock and Wildlife
To be published
Climate and Weather
To be published
Seasons
To be published
Precipitation
| Location | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mwanza | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Shinyanga | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Ngorongoro
(Serengeti) |
val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
Temperature-Heat Index
| Location | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mwanza | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Shinyanga | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Ngorongoro
(Serengeti) |
val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
Relative Humidity
| Location | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mwanza | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Shinyanga | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Ngorongoro
(Serengeti) |
val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
Wind
| Location | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mwanza | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Shinyanga | val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
| Ngorongoro
(Serengeti) |
val1 | val2 | val3 | val4 | val5 | val6 | val7 | val8 | val9 | val10 | val11 | val12 |
Summary
To be published