Difference between revisions of "Infrastructure: Olvana"
m (→Pipelines) (Tag: Visual edit) |
m (Changed "China" to "Olvana" when referring to Shanghai seaport.) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 3,545: | Line 3,545: | ||
The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan is an Olvana’s busiest in the world in terms of cargo tonnage. In 2018, The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan reported that its annual cargo throughput hit over 1.25 Billion tons of cargo. The port is located in Ningbo and Zhoushan, on the coast of the East China Sea, in Zhejiang province south of Hangzhou Bay, across which it faces Jiaxing and Shanghai. The port comprises several ports which are Beilun (seaport), Zhenhai (estuary port), and old Ningbo harbor (inland river port). The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan complex is a modern multi-purpose deep water port, consisting of inland, estuary, and coastal harbors. There are a total of 191 berths including 39 deep water berths with 10,000 and more tonnage. The larger ports include a 250,000 tonnage crude oil terminal and a 200,000+ tonnage ore loading berth. There is also a purpose-built terminal for 6th generation container vessels and a 50,000 tonnage berth dedicated for liquid chemical products. | The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan is an Olvana’s busiest in the world in terms of cargo tonnage. In 2018, The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan reported that its annual cargo throughput hit over 1.25 Billion tons of cargo. The port is located in Ningbo and Zhoushan, on the coast of the East China Sea, in Zhejiang province south of Hangzhou Bay, across which it faces Jiaxing and Shanghai. The port comprises several ports which are Beilun (seaport), Zhenhai (estuary port), and old Ningbo harbor (inland river port). The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan complex is a modern multi-purpose deep water port, consisting of inland, estuary, and coastal harbors. There are a total of 191 berths including 39 deep water berths with 10,000 and more tonnage. The larger ports include a 250,000 tonnage crude oil terminal and a 200,000+ tonnage ore loading berth. There is also a purpose-built terminal for 6th generation container vessels and a 50,000 tonnage berth dedicated for liquid chemical products. | ||
| − | The Port of Shanghai is | + | The Port of Shanghai is Olvana's most populous city, the world's second busiest seaport, and one of the world's largest cities by area. The Port of Shanghai. Located on the mouth of the Yangtze River in east Olvana off the East China Sea, the Port of Shanghai faces the East China Sea to the east, and Hangzhou Bay to the south. The Shanghai port facilities include: 125 berths with a total quay length of about 20 kilometers; 293 thousand square meters of warehouses; over 4.7 million square meters of storage yards; and 5143 units of cargo-handling equipment. The Port of Shanghai is about 421 kilometers southeast of the Port of Lianyungang and about 430 nautical miles north of the Port of Taipei in Taiwan. The Port of Shanghai is also one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world. In 2002, over 16.2 million people lived in the Port of Shanghai municipality. |
[[File:Shanghai Port.png|center|thumb|624x624px|'''<big>Shanghai Port</big>''']] | [[File:Shanghai Port.png|center|thumb|624x624px|'''<big>Shanghai Port</big>''']] | ||
| − | The Port of Shanghai is | + | The Port of Shanghai is Olvana's leading commercial and financial center, and it has been called the world's fastest-growing economy. The Port of Shanghai rivals Hong Kong as the economic heart of the Olvana mainland, but Shanghai has stronger ties to the mainland and to the central government. The Port of Shanghai also has a more solid base in the manufacturing and technology sectors. Experiencing a building boom, Shanghai's architectural style is unique and recognizable in its range of height, design, color, and unusual features. |
. | . | ||
Revision as of 11:44, 27 April 2020
DATE Pacific > Olvana > Infrastructure: Olvana ←You are here
While the region’s five major countries have a significant number of rural residents, the vast majority of Olvana’s residents live in urban areas (87%). The country contains a mixture of modern urban cities and primitive rural villages. Modern utilities are predominantly in the major cities and at reasonable levels throughout the rural countryside. Ninety-nine percent of the nation has access to electricity with 100% of urban areas and 99.8% of rural areas respectively. Ninety-five percent of Olvana has access to potable water, while only 76.5% of the nation has access to sanitation systems, predominantly in the developed urban areas.
The Olvana infrastructure is modern and continues to improve as the urbanization continues. Significant emphasis was placed on modernizing the infrastructure in the past 20 years. Olvana has a state of the art mass transit system. The Olvanan government continues to subsidize the mass transit system to increase ridership and decrease congestion on the roads and air pollution. Airports range from large international airports that can handle almost any aircraft currently in production to small, unimproved dirt strips. Seaports are modern and can handle all modern cargo vessels. The country recently suffered from high levels of pollution in the urban areas and the government has made policies to combat pollution in urban environments. Air pollution has improved significantly but ground and water pollution are still way above acceptable western levels.
Many of the urban and suburban cities contain skyscraper buildings (many over 100m tall), apartment complexes, and residential suburbs. Typical rural construction in the north is stone, tamped mud or sundried bricks reinforced with straw. In the south, the typical construction is wood, brick or woven bamboo. In both areas, the roofs are typically peaked and covered in tile. Rural houses are typically built around a courtyard. This is to provide protection from the winds and provide places to keep animals such as pigs and chickens.
Construction patterns in Olvana’s urban areas are high-rise construction and urban sprawl. The houses on the outskirts of the major urban areas are generally one to two story homes built with a courtyard in the center. The Olvanan government has invested in urban planning to ensure it is not only sustainable but with plans that go out in 5, 10, and 50 year planning cycles to ensure they stay at the forefront and can provide for growth. Due to vast amounts of rural areas, cities are not limited to just upward construction they can also continue to expand outwads.
Military operations in urban areas will initially benefit from modern electricity, water, sewage, and other utility services. Urban areas provide the additional networks of the vertical structures that will need to be dealt with as well as vast subterranean networks for transportation and infrastructure. Due to the expansive metropolitan population, Olvana will require extensive intensive urban operations.
Major Olvanan Cities and Urban Zones
Olvana has five major cities whose metropolitan areas account for approximately 40% of population of the nation. The average population density for Olvana is 311 km2.
| Infrastructure Sub-Variables | ||||||||||
| City | Population | Pop Dens/km2 | UBD | Rd | Air | Rail | Sea | Pwr | Wtr | Sani |
| Shanghai | 29,870,000 | 2,059 | H | C | C | C | C | Dv | Dv | Dv |
| Chongqing | 17,540,000 | 350 | H | C | C | C | M | Dv | Dv | Dv |
| Guangzhou | 15,720,000 | 1,800 | H | C | C | C | C | Dv | Dv | Dv |
| Wuhan | 11,140,000 | 1,200 | H | C | C | C | M | Dv | Dv | Dv |
| Hong Kong | 10,420,000 | 600 | H | C | C | C | C | Dv | Dv | Dv |
Legend (per TC-7-101): (UBD) urbanized building density, (L) low, (M) medium, (H) high,
(P) primitive, (M) moderate, (C) complex, (NE) non-existent, (Dg) degraded, (Dv) developed
Shanghai
Shanghai is the capital city and largest city in Olvana. Shanghai is also the largest city in the world. It is the financial hub of Olvana and is a global powerhouse. It has the world’s longest metropolitan transportation system with 587 km of track and tunnels. The road network is modern and the hub for the national highway network. It contains Olvana’s largest port and is a center of sea commerce. The architecture is a combination of modern steel and concrete construction and buildings dating back 1,400 years. There are over 30 universities in the city with some run by the Olvanan government. Tourism plays a significant role in the economy of the city.
Chongqing
Chongqing is located 1447 km to the west of Shanghai. The city gained major importance with the building of the Three Gorges Dam. It is built in the mountains and bordered by the Yangtze and Jialing Rivers. Chongqing has the most bridges of any area in all of Olvana with over 50 crossing the rivers, the bulk of them meeting western standards. Chongqing has 15 college and universities that range from military universities to medical schools. The city has modern skyscrapers and traditional Olvanese construction in close proximity. The downtown is a series of high-rise skyscrapers and multistory apartment buildings.
Guangzhou
Located 1447 km southwest of Shanghai, the city has been in existence for over 2,200 years and has continued to modernize throughout the years. It maintains many historic buildings and temples while becoming a modern city. The construction is concrete and steel for the skyscrapers and multistory apartment buildings. The road network is consistent with western standards. The local government continues to update the infrastructure to ensure it is capable of meeting all the demands placed on it.
Wuhan
Also located west of Shanghai, Wuhan is approximately halfway (690 km) between the capital and Chongqing. The port of Wuhan, on the Yangtze River, is currently going through a major overhaul. The Olvanan government is investing in expanding the port to increase capacity throughput from 3 berths to 22. The city has experienced a rapid growth over the past 15 years. The city planners were able to keep the infrastructure increasing at the same rate. The local government has invested heavily in environmentally friendly manufacturing and construction to decrease pollution and has made significant gains. The majority of construction is high-rise buildings for offices of steel and concrete construction. Multi story apartment buildings made of concrete and brick are throughout the city.
Hong Kong
(Hong Kong is located 1223 km south of Shanghai. The port of Hong Kong is one of the busiest ports in Olvana and the world. Three years ago, the infrastructure of Hong Kong was ranked the best in the world. The buildings throughout the city range from ones built in the late 19th century to current modern skyscrapers. As space is at a premium for construction, many old buildings have fallen into a state of disrepair and are being torn down to make way for vertical construction (skyscrapers). The main construction in the city center is modern high-rise construction. The city has a vast ferry network to transport many of the workers to the island to work every day.
Utilities Present
Olvana faces a dichotomy when it comes to utilities present such as electricity, water, and sewage treatment. The majority of urban households can access modern utilities, but the rural areas have a more limited access to a number of them. Rural areas often have a communal water source and twin vault alternating pit latrines.
Power
Over 99% of the population has access to electricity with both urban and rural populations connected to some sort of power grid. Olvana has over 1,500 power plants with a combined installed generation capacity of 929,000 MW. Most of these plants are fossil-fueled - dominated by coal, with hydroelectric being the largest renewable source. Eleven nuclear power plants account for only 3% of the country's generation capacity. Solar and wind contributions are in line with other industrialized countries.
| Fuel | Count | Capacity (MW) | Avg. Cap (MW) | Percent of Total Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 649 | 726,556 | 1,120 | 78% |
| Hydro | 408 | 73,831 | 181 | 8% |
| Natural Gas | 225 | 86,001 | 382 | 9% |
| Nuclear | 11 | 29,201 | 2,655 | 3% |
| Wind | 226 | 11,096 | 49 | 1% |
| Oil | 6 | 1,368 | 228 | <1% |
| Solar | 23 | 610 | 27 | <1% |
| Name | Fuel | Capacity (MW) | DLAT | DLONG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anwen Power Plant | Coal | 1,620 | 28.6411 | 106.7531 |
| Ayihe Yulei Hydro Plant | Hydro | 1,750 | 29.2 | 108.2 |
| Bailongmiaocun Plant | Coal | 3,400 | 35.1679 | 112.7162 |
| Banqiao Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 26.1872 | 104.1106 |
| Baofeng Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 33.8211 | 113.0146 |
| Baoshan Coal Plant | Coal | 2,520 | 31.4662 | 121.4009 |
| Beipaotai Coal Plant | Coal | 3,200 | 23.0056 | 116.5468 |
| Binhai Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 34.3071 | 120.2469 |
| Black Point Power Station | Natural Gas | 2,500 | 22.41 | 113.91 |
| Castle Peak Power Plant | Coal | 4,068 | 22.376 | 113.9214 |
| Changshu Coal Plant | Coal | 1,950 | 31.7566 | 120.979 |
| Cheliuzhuang Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 36.6656 | 119.2648 |
| Chengmai Power Plant | Coal | 2,136 | 19.9595 | 110.0317 |
| Chibi Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 29.6625 | 113.8737 |
| Dadu River Hydro Plant | Hydro | 2,600 | 29.45 | 102.22 |
| Daiwang Power Plant | Coal | 1,800 | 34.6847 | 111.0274 |
| Dakeng Reservoir Nuclear Plant | Nuclear | 1,888 | 22.6 | 114.54 |
| Daluo Hydro Plant | Hydro | 2,400 | 27.8221 | 101.9025 |
| Daqiamcun Coal Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 35.6002 | 110.5569 |
| Dashi Pan Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 6,448 | 28.6437 | 104.393 |
| Datong Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 32.6837 | 117.0753 |
| Dongbei bay Nuclear Plant | Nuclear | 4,000 | 21.71 | 112.26 |
| Dongguan Power Plant | Coal | 1,980 | 22.7489 | 113.6807 |
| Duixianmencun Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 36.1365 | 117.6876 |
| Ertan Dam | Hydro | 3,300 | 26.82 | 101.78 |
| Etouwan Coal Plant | Coal | 7,000 | 21.8664 | 112.9175 |
| Ezhou Powr Plant | Coal | 1,900 | 30.5519 | 114.6425 |
| Faerxiang Coal Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 26.3251 | 104.7695 |
| Fangchenggang Coal Plant | Coal | 2,580 | 21.5918 | 108.3947 |
| Fengtai Power Plant | Coal | 2,520 | 32.7579 | 116.6492 |
| Fuchuan Coal Plant | Coal | 2,090 | 24.7373 | 111.3464 |
| Fuxingwei Power Plant | Coal | 3,920 | 31.9403 | 120.0764 |
| Gangkou Nuclear Power Plant | Nuclear | 2,000 | 21.67 | 108.56 |
| Gangkou Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 21.7018 | 108.6227 |
| Gangouwan Hydro Plant | Hydro | 3,000 | 26.52 | 101.44 |
| Gangzha Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 32.0324 | 120.772 |
| Guangan Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 37.2684 | 118.9069 |
| Guangzhou Gangfa Terminal Power Plant | Coal | 1,900 | 22.8141 | 113.5678 |
| Guangzhou Pumped Storage Power Plant | Hydro | 2,400 | 23.7657 | 113.9536 |
| Gucheng Hydro Plant | Hydro | 1,900 | 26.53 | 100.42 |
| Gulou Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 34.3817 | 117.1756 |
| Haibeizuicun Coal Plant | Coal | 2,080 | 37.4323 | 120.0177 |
| Haiyan Nuclear Plant | Nuclear | 2,024 | 30.44 | 120.94 |
| Hanchuan Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 30.6565 | 113.9139 |
| Hanjiang Power Plant | Coal | 2,460 | 32.2684 | 119.4193 |
| Heshan Power Plant | Coal | 1,800 | 28.5971 | 112.2683 |
| Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant | Hydro | 1,920 | 20.8082 | 105.3233 |
| Houyu Islet Nuclear Plant | Nuclear | 4,000 | 25.4426 | 119.444 |
| Huainan Power Plant | Coal | 4,480 | 32.6853 | 116.9021 |
| Huangnihe Coal Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 25.1995 | 104.6826 |
| Jiangjia Mountain Power Plant | Coal | 1,800 | 28.2878 | 117.2231 |
| Jiangnan Tianchi Dam | Hydro | 1,800 | 30.47 | 119.61 |
| Jiangtun Coal Plant | Coal | 4,400 | 35.322 | 116.9292 |
| Jiaocheng Power Plant | Coal | 2,520 | 26.7575 | 119.7359 |
| Jiawang Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 34.3858 | 117.256 |
| Jingmen Nuclear Plant | Nuclear | 4,072 | 27.0446 | 120.2855 |
| Jinjiang Gas Plant | Natural Gas | 1,516 | 24.56 | 118.64 |
| Jinsha Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 13,050 | 28.2606 | 103.6484 |
| Jinshan Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 30.762 | 121.3997 |
| Jinshi Park Hydro Plant | Hydro | 3,190 | 30.7397 | 111.2695 |
| Jinxi Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 27.7855 | 116.5638 |
| Jiunvhu Plant | Coal | 3,300 | 35.467 | 112.5739 |
| Jubaowei Coal Plant | Coal | 4,000 | 32.1861 | 119.9145 |
| Jurong Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 32.1949 | 119.2494 |
| Kaercun Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 4,260 | 29.21 | 102.84 |
| Lake Nanwan Power Plant | Coal | 4,000 | 23.1885 | 116.6553 |
| Lamma Power Station | Coal | 2,250 | 22.2185 | 114.1098 |
| Lancang Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 5,850 | 22.6409 | 100.4287 |
| Lanxi Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 29.1861 | 119.5058 |
| Leigong Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 6,300 | 25.0277 | 107.0431 |
| Lianyun Nuclear Plant | Nuclear | 1,980 | 34.69 | 119.46 |
| Lirao Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 4,750 | 27.3488 | 100.5061 |
| Liuheng Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 29.7592 | 122.1262 |
| Lixin Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 32.896 | 116.2425 |
| Longgang Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 22.6059 | 114.7433 |
| Luodila Power Plant | Hydro | 2,160 | 26.2 | 100.82 |
| Luohuang Power Plant | Coal | 2,640 | 29.3467 | 106.4339 |
| Maojia Power Plant | Coal | 2,640 | 32.0577 | 121.728 |
| Mengjin Hydro Plant | Hydro | 1,800 | 34.92 | 112.36 |
| Muli Dam Hydro Plant | Hydro | 3,600 | 28.1823 | 101.6316 |
| Nanjian Hydro Facility | Hydro | 1,605 | 24.62 | 100.45 |
| Nansha Power Plant | Coal | 1,800 | 22.4818 | 113.872 |
| Ninghai Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 29.505 | 121.6627 |
| North Street Community Power Plant | Coal | 3,980 | 32.1779 | 119.5766 |
| Pacao Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 27.4974 | 120.663 |
| Panji Power Plant | Coal | 2,580 | 32.7456 | 116.8134 |
| Pinghu Power Plant | Coal | 4,400 | 30.6283 | 121.1436 |
| Pingqiao Coal Plant | Coal | 1,920 | 32.1099 | 114.1406 |
| Pudong Gas Plant | Natural Gas | 1,560 | 30.85 | 121.83 |
| Pudong Power Plant | Coal | 3,960 | 31.3508 | 121.6017 |
| Qianfeng Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 30.5298 | 106.8256 |
| Qiliuzhuangcun Coal Plant | Coal | 3,960 | 36.6148 | 116.2194 |
| Qingyuan Coal Plant | Coal | 1,920 | 27.0467 | 115.0203 |
| Qinshanzen Power Plant | Nuclear | 4,101 | 30.433 | 120.9501 |
| Qixia Power Plant | Coal | 2,060 | 32.1716 | 119.0195 |
| Quangang Coal Plant | Coal | 1,840 | 25.2038 | 118.9439 |
| Qujialong Plant | Coal | 3,320 | 31.7563 | 120.9731 |
| Sanjiancun Spillway | Hydro | 2,800 | 26.81 | 100.45 |
| Sanmen Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 29.0132 | 121.6968 |
| Shangyangxiang Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 35.5014 | 106.7871 |
| Shangyuxian Coal Plant | Coal | 2,200 | 35.8512 | 114.1781 |
| Shetou Mountain Coal Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 26.3736 | 119.7621 |
| Shifeng Power Plant | Coal | 1,820 | 27.8592 | 113.1195 |
| Shiheng Coal Plant | Coal | 1,800 | 36.2122 | 116.512 |
| Shishi Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 24.7277 | 118.7478 |
| Shizhong Power Plant | Coal | 2,060 | 34.8144 | 117.5743 |
| Shuanghuaizhen Power Plant | Coal | 1,920 | 30.1621 | 106.5474 |
| Shubuyazhen Hydro Plant | Hydro | 1,600 | 30.44 | 110.34 |
| Son La Hydropower | Hydro | 2,400 | 21.4971 | 103.996 |
| Strong Islands Coal Plant | Coal | 4,400 | 29.481 | 121.5109 |
| Suanshanqi Power Plant | Coal | 5,000 | 29.9433 | 121.815 |
| Taicang Power Plant | Coal | 1,880 | 31.6566 | 121.1799 |
| Three Gorges Dam | Hydro | 22,500 | 30.8235 | 111.0032 |
| Tongluodan Power Plant | Coal | 3,200 | 22.7061 | 115.5543 |
| Wisicun Coal Plant | Coal | 1,920 | 37.0089 | 114.4842 |
| Wolong Power Plant | Coal | 1,900 | 33.3082 | 112.6451 |
| Wujiang Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 3,000 | 27.3744 | 107.633 |
| Wushizhen Power Plant | Coal | 2,100 | 24.5852 | 113.5831 |
| Xiadakeng Nuclear Plant | Nuclear | 3,914 | 22.6 | 114.55 |
| Xiangcheng Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 31.9122 | 112.1662 |
| Xiangshui Power Plant | Coal | 2,400 | 25.4692 | 104.5912 |
| Xiaoaotou Wei Plant | Coal | 3,600 | 24.3048 | 118.1261 |
| Xiaomo Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 22.7563 | 115.0426 |
| Xiaoshantou Coal Plant | Coal | 4,200 | 28.1142 | 121.1398 |
| Xiaqi Hydro Plant | Hydro | 2,400 | 23.27 | 114.31 |
| Xiazhari Plant | Hydro | 2,400 | 27.68 | 100.29 |
| Xidaling Power Plant | Coal | 2,660 | 34.5782 | 119.1275 |
| Xintian Coal Plant | Coal | 2,100 | 30.6777 | 108.4004 |
| Xisaishan Power Plant | Coal | 2,020 | 30.2031 | 115.1803 |
| Xiuyu Coal Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 25.157 | 119.0289 |
| Xiuyu Gas Plant | Natural Gas | 1,528 | 25.22 | 119 |
| Yalong Hydroelectric Plant | Hydro | 4,400 | 28.2485 | 101.6445 |
| Yangxi Power Plant | Coal | 2,520 | 21.5454 | 111.6678 |
| Yanwan Power Plant | Hydro | 2,100 | 29.31 | 103.48 |
| Yingjiang Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 30.5414 | 117.1746 |
| Yongchicun Coal Plant | Coal | 2,640 | 36.8972 | 117.8613 |
| Yuncheng Power Plant | Coal | 2,000 | 22.9657 | 112.1079 |
| Yuzhou Powerl Plant | Coal | 2,020 | 34.1748 | 113.3565 |
| Zhangshu Power Plant | Coal | 2,520 | 28.1957 | 115.7097 |
| Zhelinzhen Plant | Coal | 3,200 | 23.5655 | 117.0973 |
| Zhenhai Power Plant | Coal | 1,560 | 29.9445 | 121.6869 |
| Zhongbazhen Power Plant | Coal | 1,960 | 31.8045 | 104.7679 |
| Zhuziba Hydro Plant | Hydro | 2,400 | 27.82 | 101.88 |
Water
Nearly all of the Olvanan population in urban areas (97.5%) has access to improved potable water. As areas become more rural, only 93% have access relying on local sources (rivers and streams) or community wells.
The urbanization of the population has caused significant strain on water delivery systems; the government has initiated projects to improve the water quality and access. In many of the rural areas, the water is polluted from spills from either factories, raw sewage or illegal dumping. Rural Olvanans have nearly over 10% of their water supply that is not safe to use even for irrigation due to heavy metal contamination. Military personnel should find potable water in the urban areas but may see a shortage in the rural areas. Prior to use of any local water source they should be tested and potentially treated for contamination.
Sanitation
Olvanans that reside in urban areas have access to some sort of sewage system with 86.6% of residents having access to improved sanitation services and 13.4% having access to unimproved facilities (pit latrines). In rural areas, only 63.7% of the population has access to improved sewage (septic / modern pipes); the remaining 36.3% have access to twin vault alternating pit latrines. Only a small portion of the wastewater is treated which has led to contamination of 61.5% of groundwater and 28.8% of key rivers being determined to be not suitable for human contact. Due to limited wastewater treatment facilities, most domestic wastewater is discharged without treatment. Five years ago the government dramatically increased the emphasis on reducing pollution to include water contamination. The government has several projects approved for modernizing the sewage system in both urban and rural areas.
Transportation Architecture
Roads are the primary transportation method throughout Olvana. The rail network of the country is very modern as it has been upgraded or installed in the past 15 years to support mass transit. The government has invested and subsidized mass transit over the past 12 years to help reduce pollution and congestion. The majority of roads are in good condition as they are paid for through a toll system and private companies.
Road Systems
Overall, roads in Olvana meet US or Western European standards. The exception will be in the rural and smaller villages that still have something little wider than a footpath to get through. Driving can be hazardous as the enforcement of traffic laws vary greatly across the nation. In general, drivers drive chaotic and unregulated; Olvana has one of the highest rate of accidents in the region. Of note, pedestrians do not have the right of way when crossing a road (even at a crosswalk). Due to large amounts of congestion on the roadways, the drivers will drive very aggressively.
Olvana has a vast national road network of 4,602,150 km that includes 4,100,225 km of paved roads. The road network consists mainly of three types of national roads: Freeways, Olvana National Highways, and Express Routes. Freeways are toll roads that are unencumbered by stoplights / signs with separated cross traffic. Olvana National Highways are trunk roads across the country that may have portions that are toll roads. Express routes run through major urban areas. The government of Olvana does not maintain any of the road networks as that is left to for-profit businesses and the local cities, towns, and villages. Most urban roads have heavy traffic and are viewed as dangerous because of aggressive driving habits.
Military traffic / convoys on the road networks will be stressed due to large amounts of traffic and the aggressive driving nature of the Olvanans and impatience to wait in traffic.
Bus
All towns and villages have at least daily bus traffic through the area. The majority of urban areas will have multiple bus stations that have regularly scheduled departure to points around the city or cross-country routes. The bus companies are independently owned and operated. The buses run both in the major metropolitan areas and to the more rural areas. Due to the relatively low cost of other methods of public transportation (bullet trains / subway), buses are typically used for shorter distance travel within major urban areas and between rural towns and villages.
Buses operate throughout Olvana, providing mainly travel to the civilian population within the urban areas. Very few Olvanans use them for long distance travel, as there are other more efficient and reliable ways to move around the nation. The buses used by the private companies do not come from any predominant company. Many of the buses have air conditioning and have been upgraded to be electric for operation in the city. Many of the major bus companies originate their lines from the major metropolitan areas and then run to the more rural areas. The Olvanan government has been subsidizing the bus system to help pay for upgrades to the mass transit system and in an effort to decrease pollution.
Any military operations in the country that affect the bus system may cause strain on the mass transportation system and cause extended delays resulting in a decreased perception of military forces by the civilian population.
Rail
The country has 110,000 km of rail in the country, with 75,000 km of rail currently electrified and 22,000 km being high speed rail. Olvana approved several projects to modernize the rail system over the past 15 years to improve commuter travel throughout the nation. The main project is a high-speed rail line to help decrease pollution and congestion throughout the country. Olvana rail consists of standard gauge (1.435 m) which is in use by the neighboring countries. The locomotives used in Olvana are diesel or electric. Of note, 28 of 33 provinces are connected by high speed rail.
Air Transportation Systems
Olvana maintains 245 paved airfields, 88 of which are strictly military bases. There are also numerous helipads/heliports located throughout the urban areas. Very little is known about the many unpaved/unmaintained facilities found throughout the country. Less than 33 percent of the airspace is allocated to civilian aircraft, reduced to 25 percent during military exercises. This compounds the delays and cancellations that are part of normal air travel in Olvana.
Paved Runways
- Over 10,000 feet: 69
- 8,000 to 10,000 feet: 86
- 5,000 to 8,000 feet: 79
- 3,000 to 5,000 feet: 9
- Under 3000 feet: 2
Airfield Data
| City | Military Air Base | Rwy Length
(ft) |
Rwy Width
(ft) |
Elev
(ft) |
DLAT | DLONG | Surface | Lights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankang | 5249 | 148 | 860 | 32.7081 | 108.9310 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Anqing | 9186 | 148 | 29 | 30.5822 | 117.0500 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Anshun | 9186 | 150 | 4812 | 26.2606 | 105.8733 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Anyang | 3223 | 208 | 226 | 36.1339 | 114.3440 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Bắc Giang | 6000 | 120 | 46 | 21.3897 | 106.2525 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Baise | 8202 | 148 | 148 | 23.7206 | 106.9600 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Beihai | 10499 | 150 | 69 | 21.5394 | 109.2940 | Cement | Yes | |
| Bengbu | 8818 | 168 | 100 | 32.8477 | 117.3202 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Bijie | 8530 | 148 | 4751 | 27.2671 | 105.4721 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Changde | 8366 | 164 | 128 | 28.9189 | 111.6400 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Changsha | 12467 | 148 | 217 | 28.1892 | 113.2200 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Changsha | 8290 | 164 | 170 | 28.0689 | 112.9580 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Changzhi | 8530 | 148 | 1250 | 36.2475 | 113.1260 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Changzhou | 11155 | 164 | 30 | 31.9197 | 119.7790 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Chengdu | 11811 | 197 | 1625 | 30.5785 | 103.9470 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Chizhou | 7874 | 140 | 60 | 30.7403 | 117.6856 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Chongqing | 12467 | 148 | 1365 | 29.7192 | 106.6420 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Dali | 8202 | 142 | 7050 | 25.6494 | 100.3190 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Danfeng | 4273 | 110 | 2382 | 33.7085 | 110.2493 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Daocheng | 13780 | 197 | 14472 | 29.3231 | 100.0533 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Dazhou | 6562 | 148 | 1013 | 31.1302 | 107.4295 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Điện Biên Phủ | 6003 | 100 | 1611 | 21.3975 | 103.0080 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Enshi | 6890 | 150 | 1605 | 30.3203 | 109.4850 | Paved | Yes | |
| Foshan | 9186 | 150 | 6 | 23.0833 | 113.0700 | Cement | Yes | |
| Fuyang | 7874 | 140 | 104 | 32.8822 | 115.7344 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Fuzhou | 11841 | 150 | 46 | 25.9351 | 119.6630 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Ganzhou | 8530 | 148 | 387 | 25.8533 | 114.7789 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Golog | 12467 | 148 | 12428 | 34.4181 | 100.3011 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guanghan | 7392 | 150 | 1531 | 30.9485 | 104.3296 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Guangyuan | 13780 | 197 | 14472 | 32.3911 | 105.7020 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guangzhou | 12467 | 148 | 49 | 23.3924 | 113.2990 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guilin | 10499 | 147 | 571 | 25.2181 | 110.0390 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guiyang | 10500 | 197 | 3737 | 26.5385 | 106.8010 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guyuan | 9186 | 148 | 5577 | 36.0789 | 106.2169 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Haikou | 11811 | 148 | 75 | 19.9349 | 110.4590 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Haiphong | 8200 | 131 | 50 | 20.8034 | 106.6050 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Haiphong | 10007 | 164 | 6 | 20.8194 | 106.7250 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Handan | 7218 | 148 | 229 | 36.5258 | 114.4256 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hangzhou | 10499 | 150 | 12 | 30.3353 | 120.2410 | Cement | Yes | |
| Hangzhou | 11811 | 197 | 23 | 30.2295 | 120.4340 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hanoi | 12466 | 148 | 39 | 21.2212 | 105.8070 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hanzhong | 8202 | 164 | 1677 | 33.1341 | 107.2060 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hechi | 7218 | 148 | 2221 | 24.8050 | 107.6997 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hefei | 11155 | 164 | 108 | 31.7800 | 117.2980 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hengyang | 8530 | 148 | 216 | 26.9053 | 112.6280 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hong Kong | 12467 | 150 | 0 | 22.3086 | 113.9182 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Hong Kong | 12467 | 197 | 28 | 22.3089 | 113.9150 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hongyuan | 11811 | 150 | 11598 | 32.5315 | 102.3522 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Huai'an | 7874 | 148 | 23 | 33.7908 | 119.1250 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Huaihua | 7218 | 164 | 882 | 27.4411 | 109.7000 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Huangping | 8530 | 160 | 3115 | 26.9720 | 107.9880 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Huangshan | 8530 | 150 | 3300 | 29.7333 | 118.2560 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Huangyan | 8202 | 148 | 32 | 28.5622 | 121.4290 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Huizhou | 7874 | 150 | 50 | 23.0500 | 114.6000 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Ji'an | 10499 | 148 | 281 | 26.8569 | 114.7370 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jinan | 11814 | 148 | 76 | 36.8572 | 117.2160 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jingdezhen | 7874 | 148 | 112 | 29.3386 | 117.1760 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jingzhou | 6019 | 148 | 112 | 30.3243 | 112.2799 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Jining | 9186 | 150 | 134 | 35.2928 | 116.3467 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jiujiang | 9596 | 148 | 164 | 29.4769 | 115.8011 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jiuzhaigou | 10499 | 150 | 11312 | 32.8533 | 103.6822 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Kangding | 13123 | 197 | 14042 | 30.1299 | 101.7518 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Kunming | 14764 | 148 | 6903 | 25.1019 | 102.9292 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Kunming | 11088 | 158 | 6221 | 24.9924 | 102.7435 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lanzhou | 11811 | 150 | 6388 | 36.0333 | 103.8667 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Leshan | 4555 | 148 | 1230 | 29.7334 | 103.6122 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Liangping | 7498 | 147 | 1493 | 30.6794 | 107.7860 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lianyungang | 8202 | 148 | 7 | 34.5717 | 118.8736 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lijiang | 9843 | 148 | 7359 | 26.6800 | 100.2460 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Linfen | 8530 | 148 | 1483 | 36.1326 | 111.6412 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Linyi | 7546 | 150 | 244 | 35.0461 | 118.4120 | Paved | Yes | |
| Liping | 7181 | 148 | 1620 | 26.3222 | 109.1499 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Liuzhou | 8202 | 164 | 295 | 24.2075 | 109.3910 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Longyan | 7874 | 150 | 1225 | 25.6747 | 116.7470 | Cement | Yes | |
| Louding | 4610 | 93 | 190 | 22.7112 | 111.6013 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Luoyang | 8202 | 148 | 840 | 34.7411 | 112.3880 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Luzhou | 7874 | 148 | 860 | 28.8522 | 105.3930 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Macau | 11024 | 148 | 20 | 22.1496 | 113.5920 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Meizhou | 7874 | 148 | 259 | 24.3500 | 116.1330 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Mianyang | 7874 | 165 | 1552 | 31.4281 | 104.7410 | Cement | Yes | |
| Nanchang | 11155 | 148 | 144 | 28.8650 | 115.9000 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Nanchang | 8395 | 164 | 122 | 28.6356 | 115.9300 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Nanchong | 7874 | 148 | 1115 | 30.7955 | 106.1626 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Nanjing | 11811 | 148 | 49 | 31.7420 | 118.8620 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Nanning | 10499 | 148 | 420 | 22.6083 | 108.1720 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Nantong | 11155 | 164 | 16 | 32.0708 | 120.9760 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Nanyang | 9186 | 164 | 840 | 32.9808 | 112.6150 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Ningbo | 10499 | 148 | 13 | 29.8267 | 121.4620 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Ninglang | 11155 | 164 | 10804 | 27.5403 | 100.7593 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Panzhihua | 9186 | 148 | 6496 | 26.5400 | 101.7985 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Pucheng | 4317 | 148 | 771 | 34.8333 | 109.5443 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Pu'er | 8104 | 165 | 4285 | 22.7933 | 100.9590 | Cement | Yes | |
| Qianjiang | 7874 | 148 | 2075 | 29.5133 | 108.8311 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Qingdao | 11155 | 148 | 33 | 36.2661 | 120.3740 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Qingyang | 5791 | 165 | 39 | 35.7997 | 107.6030 | Paved | Yes | |
| Qionghai | 10499 | 164 | 30 | 19.1382 | 110.4548 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Quanzhou | 8530 | 148 | 46 | 24.7964 | 118.5900 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Qujing | 5000 | 150 | 6145 | 25.5922 | 103.8290 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Quzhou | 8202 | 148 | 253 | 28.9658 | 118.8990 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Rizhao | 8530 | 148 | 121 | 35.4050 | 119.3244 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Sam Neua | 3715 | 80 | 3281 | 20.4184 | 104.0670 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Sanming | 8530 | 150 | 830 | 26.4263 | 117.8336 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Sanya | 11155 | 148 | 92 | 18.3029 | 109.4120 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shanghai | 11154 | 148 | 10 | 31.1979 | 121.3360 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shanghai | 13123 | 197 | 13 | 31.1434 | 121.8050 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shangrao | 7874 | 148 | 340 | 28.3797 | 117.9643 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shangri-La | 11647 | 150 | 10761 | 27.7936 | 99.6772 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shantou | 8202 | 148 | 29 | 23.4269 | 116.7620 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shantou | 9186 | 148 | 167 | 23.5520 | 116.5033 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shaoguan | 7075 | 150 | 280 | 24.9786 | 113.4210 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shennongjia | 9186 | 148 | 8465 | 31.6260 | 110.3400 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shenzhen | 12467 | 148 | 13 | 22.6393 | 113.8110 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shiyan | 8530 | 148 | 810 | 32.5917 | 110.9078 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Sơn La | 7874 | 135 | 2133 | 21.2170 | 104.0330 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Suining | 3918 | 96 | 954 | 30.4713 | 105.6109 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Suzhou | 7218 | 148 | 16 | 31.2631 | 120.4010 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Thanh Hoá | 10535 | 150 | 377 | 19.9028 | 105.4700 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Tianshui | 9186 | 150 | 3590 | 34.5594 | 105.8600 | Cement | Yes | |
| Tongren | 9022 | 150 | 863 | 27.8833 | 109.3089 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Vinh | 7875 | 148 | 23 | 18.7376 | 105.6710 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Wanzhou | 7874 | 148 | 1860 | 30.8017 | 108.4330 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Weifang | 8530 | 148 | 156 | 36.6467 | 119.1190 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Weihai | 8530 | 148 | 145 | 37.1871 | 122.2290 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Wenshan | 7874 | 148 | 5217 | 23.5583 | 104.3255 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Wenzhou | 10499 | 150 | 24 | 31.4944 | 120.4290 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Wuhan | 11811 | 148 | 113 | 30.7838 | 114.2080 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Wuxi | 10499 | 197 | 16 | 31.4992 | 120.4300 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Wuyishan | 7874 | 150 | 643 | 27.7019 | 118.0010 | Cement | Yes | |
| Wuzhou | 5906 | 148 | 89 | 23.4567 | 111.2480 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xiahe | 10499 | 150 | 10509 | 34.8105 | 102.6447 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xiamen | 11155 | 148 | 59 | 24.5440 | 118.1280 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Xi'an | 12467 | 148 | 1572 | 34.4471 | 108.7520 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xiangyang | 7874 | 150 | 9603 | 32.1506 | 112.2910 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Xichang | 11811 | 164 | 5112 | 27.9891 | 102.1840 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xingning | 8500 | 130 | 7464 | 24.1492 | 115.7580 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xingtai | 8530 | 148 | 280 | 36.8831 | 114.4293 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xingyi | 7546 | 148 | 4150 | 25.0864 | 104.9594 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Xuzhou | 11155 | 147 | 108 | 34.0591 | 117.5553 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yancheng | 9186 | 164 | 3 | 33.4258 | 120.2031 | Cement | Yes | |
| Yangzhou | 7874 | 150 | 7 | 32.5634 | 119.7198 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yantai | 11155 | 148 | 59 | 37.4017 | 121.3720 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yibin | 7054 | 148 | 924 | 28.8006 | 104.5450 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yichang | 5211 | 87 | 235 | 30.6710 | 111.4404 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Yichang | 8530 | 148 | 673 | 30.5566 | 111.4800 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yichun | 7874 | 148 | 430 | 27.8025 | 114.3062 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yiwu | 9843 | 175 | 262 | 29.3447 | 120.0320 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yongji | 7814 | 147 | 1236 | 34.8723 | 110.3610 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yongzhou | 8530 | 148 | 340 | 26.3387 | 111.6100 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yuncheng | 9843 | 164 | 1242 | 35.1164 | 111.0314 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zhangjiajie | 8530 | 150 | 692 | 29.1028 | 110.4430 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zhanjiang | 7874 | 148 | 125 | 21.2144 | 110.3580 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Zhaotong | 5280 | 164 | 6319 | 27.3256 | 103.7550 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Zhengzhou | 11811 | 197 | 495 | 34.5197 | 113.8410 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zhoushan | 7546 | 150 | 3 | 29.9342 | 122.3620 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zhuhai | 13517 | 197 | 23 | 22.0064 | 113.3760 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zigong | 4188 | 100 | 1133 | 29.3765 | 104.6258 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zunyi | 9186 | 148 | 2920 | 27.5895 | 107.0007 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Baihe Ning Ming Air Base | 7181 | 148 | 0 | 22.1206 | 107.1250 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Baitabu Air Base | 8131 | 148 | 20 | 34.5714 | 118.8750 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Baoji Air Base | 5861 | 150 | 1870 | 34.5317 | 107.4720 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Chang-Chou Airfield | 7762 | 164 | 9603 | 24.5625 | 117.6540 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Changzing Air Base | 7550 | 148 | 502 | 30.9686 | 119.7310 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Chengdu Air Base | 8079 | 150 | 1640 | 30.7053 | 103.9503 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Chongqing Air Base | 7500 | 148 | 801 | 29.4953 | 106.3590 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Daishan Air Base | 7498 | 148 | 118 | 30.2878 | 122.1450 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Dali Air Base | 8450 | 150 | 6480 | 25.6500 | 100.3192 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Dangyang Air Base | 9134 | 164 | 292 | 30.7986 | 111.8100 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Dazu Air Base | 6970 | 150 | 1220 | 29.6362 | 105.7736 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Dingxi Air Base | 13306 | 164 | 6243 | 40.4019 | 99.7911 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Feidong Air Base | 8553 | 164 | 123 | 31.9094 | 117.6590 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Foluo Northeast Air Base | 8818 | 164 | 449 | 18.6922 | 109.1610 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Fouliang Air Base | 7867 | 150 | 171 | 29.3394 | 117.1767 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Fuzhou Air Base | 8026 | 150 | 45 | 26.0044 | 119.3120 | Cement | Yes | |
| Gaomi Air Base | 7762 | 148 | 79 | 36.3869 | 119.7181 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Gia Lam Airbase | 6565 | 150 | 50 | 21.0410 | 105.8860 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Guanghua Air Base | 10771 | 197 | 305 | 32.3894 | 111.6950 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guangzhou Air Base | 10771 | 164 | 68 | 32.3889 | 111.6950 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guanzhou East Airfield | 5280 | 150 | 68 | 23.1647 | 113.3690 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Guilin-Tannan Air Base | 8078 | 148 | 502 | 25.1939 | 110.3206 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Guiping Mengshu Air Base | 9610 | 150 | 164 | 23.3308 | 110.0090 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Guiyang Air Base | 10560 | 164 | 3600 | 26.4099 | 106.5323 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hanoi Air Base | 6571 | 100 | 50 | 21.0405 | 105.8860 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Hòa Lạc Air Base | 5597 | 120 | 76 | 21.0383 | 105.4899 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Hong Kong Air Base | 6180 | 110 | 50 | 22.4366 | 114.0800 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Huian Air Base | 7550 | 148 | 46 | 25.0261 | 118.8070 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jialaishi Air Base | 9610 | 197 | 98 | 19.6972 | 109.7260 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jiaozhou Air Base | 9187 | 148 | 32 | 36.3306 | 120.0240 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jiaxing Air Base | 8923 | 148 | 26 | 30.7066 | 120.6806 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Jinjiang Air Base | 8448 | 148 | 108 | 24.7975 | 118.5883 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Kaifeng Air Base | 8125 | 148 | 245 | 34.7539 | 114.3390 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Kaiyang Guiyang Air Base | 10507 | 164 | 3600 | 26.5392 | 106.8014 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Kashi Air Base | 10349 | 164 | 4167 | 39.5414 | 76.0192 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Kep Air Base | 7230 | 150 | 55 | 21.3946 | 106.2610 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Laiyang Air Base | 7181 | 148 | 131 | 36.9636 | 120.5910 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lanzhou Air Base | 9504 | 295 | 4980 | 35.9178 | 104.2180 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Leiyang Air Base | 10138 | 164 | 226 | 26.5872 | 112.8920 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lingshui Air Base | 10032 | 164 | 12 | 18.4944 | 109.9880 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lintao Air Base | 10243 | 173 | 6178 | 35.3083 | 103.8360 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lintong Air Base | 9557 | 148 | 1394 | 34.3761 | 109.1211 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Liujiang-Liuzhou Air Base | 8290 | 148 | 361 | 24.2089 | 109.3913 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Longyou Air Base | 6180 | 85 | 253 | 29.1131 | 119.1770 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Luliang Air Base | 8698 | 150 | 3123 | 24.9883 | 103.6420 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Lung-T'ien Air Base | 7498 | 148 | 82 | 25.5728 | 119.4600 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Luyang Air Base | 7181 | 148 | 457 | 33.6847 | 112.8910 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Mahuiling Air Base | 9398 | 148 | 66 | 29.4772 | 115.8020 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Meixian Air Base | 7762 | 164 | 259 | 24.2650 | 116.1000 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Mengzi Air Base | 8131 | 150 | 4300 | 23.3953 | 103.3340 | Paved | Yes | |
| Nanchang Air Base | 8026 | 148 | 122 | 28.4208 | 115.9240 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Nanjing Air Base | 11458 | 150 | 39 | 31.9983 | 118.8120 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Ningbo Zhuangqiao Air Base | 8184 | 150 | 488 | 29.9228 | 121.5740 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Qingdao Naval Base | 870 | 120 | 0 | 36.0469 | 120.2840 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Qingdao-Cangkou Air Base | 2945 | 164 | 210 | 36.1592 | 120.3920 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Qingshui Air Base | 9715 | 148 | 16 | 39.5547 | 98.8842 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Qionglai Air Base | 10718 | 197 | 1640 | 30.4900 | 103.4650 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Queshan Air Base | 8765 | 130 | 256 | 32.5408 | 114.0791 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Rugao Air Base | 7339 | 148 | 26 | 32.2579 | 120.5017 | Concrete | Yes | |
| San Bay Air Base | 7181 | 169 | 82 | 21.7348 | 104.8527 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Shanghai Chongming Air Base | 8553 | 148 | 13 | 31.6617 | 121.5183 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shanghai Dachang Air Base | 9662 | 164 | 13 | 31.3236 | 121.4110 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shangqiu Air Base | 7867 | 148 | 184 | 34.4495 | 115.4593 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shanpo Airfield | 7656 | 148 | 1568 | 30.0881 | 114.3144 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shantou Northeast Airfield | 8202 | 148 | 167 | 23.4272 | 116.7592 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Shek Kong Airfield | 6250 | 110 | 50 | 22.4367 | 114.0803 | Paved | Yes | |
| Simao North Airfield | 8131 | 164 | 4285 | 22.7939 | 100.9592 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Suixi Air Base | 9186 | 164 | 112 | 21.3958 | 110.2000 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Tunxi Airstrip | 5280 | 150 | 121 | 29.7328 | 118.2569 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Wenshan Air Base | 8026 | 148 | 4124 | 23.7156 | 103.8270 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Wugong Air Base | 9821 | 148 | 1270 | 34.2742 | 108.2660 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Wuhu Air Base | 7814 | 148 | 26 | 31.3906 | 118.4090 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Wuyishan Air Base | 7339 | 148 | 643 | 27.7003 | 118.0000 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xian Air Base | 7286 | 148 | 1329 | 34.1539 | 108.5990 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xiangyun Midu Air Base | 9134 | 164 | 232 | 25.4453 | 100.7350 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xiaogan Air Base | 5065 | 128 | 115 | 30.9544 | 113.9110 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xincheng Air Base | 6811 | 148 | 141 | 25.5483 | 114.6190 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xuzhou Daguozhang Air Base | 11035 | 164 | 954 | 34.0589 | 117.5580 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Xuzhou Jiulishan Air Base | 7286 | 148 | 30 | 34.2306 | 117.2460 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yancheng Air Base | 8923 | 164 | 3 | 37.1858 | 122.2297 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yanliang Air Base | 11035 | 148 | 1296 | 34.6439 | 109.2430 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yantai Southwest Air Base | 10613 | 150 | 72 | 37.3997 | 121.3689 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yên Bái Air Base | 9170 | 150 | 2000 | 21.7351 | 104.8527 | Paved | Yes | |
| Yidu Air Base | 4867 | 140 | 322 | 36.5914 | 118.5270 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Yuanmou Air Base | 9240 | 135 | 3810 | 25.7375 | 101.8820 | Asphalt | Yes | |
| Zhangshu Air Base | 11986 | 197 | 325 | 28.0217 | 115.5510 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zhengzhou Air Base | 8448 | 164 | 374 | 34.8613 | 113.7296 | Concrete | Yes | |
| Zhucheng Air Base | 7814 | 164 | 215 | 36.0275 | 119.4390 | Concrete | Yes |
Airlines
Air Olvana Airlines is the flagship carrier for Olvana. Air Olvana Airlines flies internationally to 14 countries across the world. Multiple international airports operate in Olvana predominately on the east coast and central area. Olvana possesses enough airports to support major military operations. Domestically, airlines do not travel on time and are plagued with cancelled flights and hours long delays.
Maritime Seaports
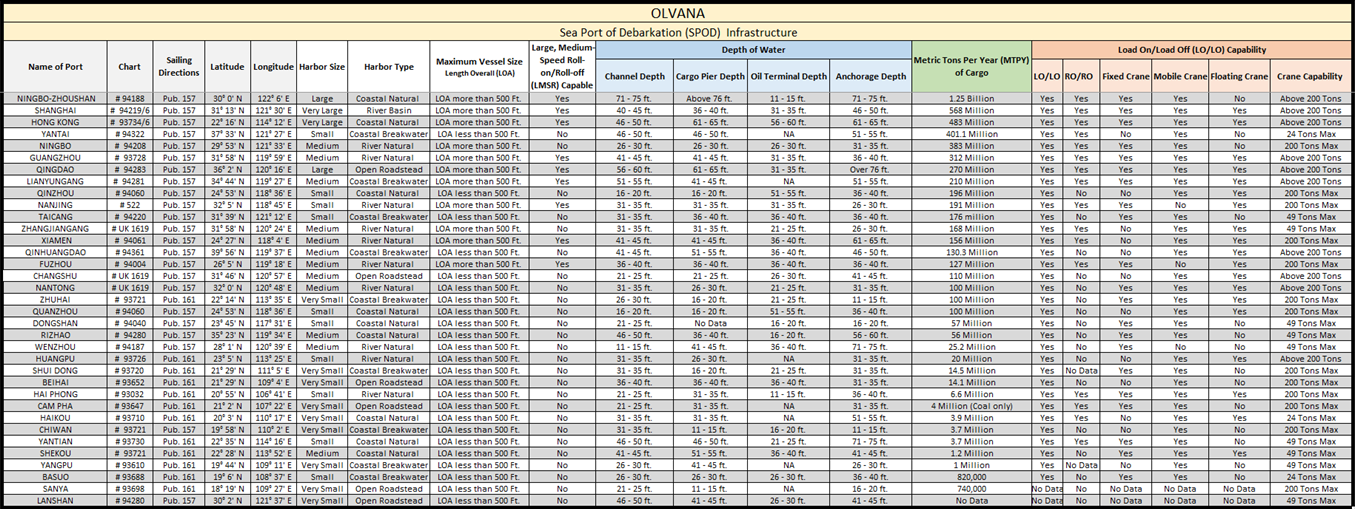
In 2018, the driving force behind the acceleration in global port volumes was the global economic powerhouse, Olvana. The intrinsic link between the health of the country’s economy and global containerized trade was once again evident in the top 100 ports rankings, which comprised no fewer than 22 Olvana entries. Olvana has 35 major seaports and more than 2000 minor ports located along the South China Sea, East China Sea, and the Yellow Sea. Ovana’s major ports are mostly sea ports (except for ports such as Shanghai, Nanjing and Nantong along the Changjiang River and Guangzhou in the Pearl river delta) opening up to the Yellow sea (Bo Hai), Taiwan straits, Pearl river and South Olvana Sea while the latter comprise ports that lie along the major and minor rivers of Olvana. Most of Olvana’s major cities are also ports or are facilitated by a port nearby. Olvana’s coastal ports enable the transportation of coal, containers, imported iron ore, and grain; roll-on-roll-off operations between mainland and islands; and deep-water access to the sea. In port construction, Olvana has especially strengthened the container transport system, concentrating on the construction of a group of deep-water container wharves at Ningbo-Zhoushan, Qingdao, Shanghai, Ningbo, Xiamen and Hong Kong, and thus laying the foundations for Olvana’s container hubs. There are 32 Olvana ports that average more than 1 million tons of cargo throughput annually. Olvana has a total of 9 ports that can accommodate a Military Sea Lift (MSC) Commands Large, Medium-Speed Roll-on/Roll-off (LMSR).
The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan is an Olvana’s busiest in the world in terms of cargo tonnage. In 2018, The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan reported that its annual cargo throughput hit over 1.25 Billion tons of cargo. The port is located in Ningbo and Zhoushan, on the coast of the East China Sea, in Zhejiang province south of Hangzhou Bay, across which it faces Jiaxing and Shanghai. The port comprises several ports which are Beilun (seaport), Zhenhai (estuary port), and old Ningbo harbor (inland river port). The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan complex is a modern multi-purpose deep water port, consisting of inland, estuary, and coastal harbors. There are a total of 191 berths including 39 deep water berths with 10,000 and more tonnage. The larger ports include a 250,000 tonnage crude oil terminal and a 200,000+ tonnage ore loading berth. There is also a purpose-built terminal for 6th generation container vessels and a 50,000 tonnage berth dedicated for liquid chemical products.
The Port of Shanghai is Olvana's most populous city, the world's second busiest seaport, and one of the world's largest cities by area. The Port of Shanghai. Located on the mouth of the Yangtze River in east Olvana off the East China Sea, the Port of Shanghai faces the East China Sea to the east, and Hangzhou Bay to the south. The Shanghai port facilities include: 125 berths with a total quay length of about 20 kilometers; 293 thousand square meters of warehouses; over 4.7 million square meters of storage yards; and 5143 units of cargo-handling equipment. The Port of Shanghai is about 421 kilometers southeast of the Port of Lianyungang and about 430 nautical miles north of the Port of Taipei in Taiwan. The Port of Shanghai is also one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world. In 2002, over 16.2 million people lived in the Port of Shanghai municipality.
The Port of Shanghai is Olvana's leading commercial and financial center, and it has been called the world's fastest-growing economy. The Port of Shanghai rivals Hong Kong as the economic heart of the Olvana mainland, but Shanghai has stronger ties to the mainland and to the central government. The Port of Shanghai also has a more solid base in the manufacturing and technology sectors. Experiencing a building boom, Shanghai's architectural style is unique and recognizable in its range of height, design, color, and unusual features.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Pipelines
Olvana has 70,000 km of gas pipelines, 20,000 km of crude oil pipelines, 23,000 km of refined petroleum products pipelines, and 700,000 km of water pipelines. The gas pipelines run along the eest coast from the southernmost point to the northern border, they also run from the northeast boarder to Shanghai. Three of the pipelines cross in to adjacent countries. The crude oil pipelines follow generally the same routes. These pipelines are government owned and operated. The gas pipelines are extremely vital to the infrastructure as they provide the natural gas to use for heat and power and move away from coal.
Telecommunications Architecture
In Olvana, almost all citizens can access a telephone and listen to a radio or television, and over 54% of the population has access to the internet. Approximately 10 years ago, the country's six telecommunications companies were merged to create three telecommunications companies. Olvanans operate approximately 230 million landlines and a billion cell phones. The country has approximately 1000 television stations that are all government owned and operated. Cable is the main provider of television channels.
Industry
The Olvana industrial complex is the number one producer of steel in the world and the largest consumer / producer of chemicals, accounting for one-third of the global demand. Manufacturing gnerates roughly 46.6 percent of the GDP. The government relaxing some of the restrictions on private investments and ownership has caused an increase in industries. Military operations must be aware of the manufacturing areas and ensure not to disrupt them.
Agriculture
Over a third of Olvanans engage in agricultural work, which accounts for only 10 percent of the country’s GDP. The bulk of Olvanan farms are medium sized farms. The major agriculture productions in the country are wheat, sorghum, millet, barley, soybeans, rice, and radishes. The current agriculture production is sufficient to sustain the population and the country exports grains and meat to meet the demand of the populace. However, due to high demand exceeding domestic production, the nation imports rice.
Oil/Gas
Olvana is the world’s largest oil importer. It comes from a pipeline in the north and is brought by ships to the ports. Olvana has a very large oil infrastructure that produces approximately 10,155,000 barrels of crude a day. The country must import oil to meet the demand in the country, which is equivalent to 960,000 barrels a day of oil to remain functioning. There has been exploration done in the contested South China Sea to locate more oil but there has been limited success.
Military operations in the area must ensure that oil is imported to support the economy and citizens of the country to ensure development during and post hostilities.
Olvana has been producing more natural gas than it has at any point in the past 40 years and it still does not meet the demand in the country. There are two main pipelines that import natural gas from neighboring countries. The shift to cleaner burning fuels is done in response to moving away from coal to decrease air pollution. Neighboring countries have the ability to shut off the pipelines in the event of hostilities.
Defense Industries
The defense industry in Olvana is growing with the recent opening of the defense industry to commercial investors. This defense industry exports aircraft, tankers, air defense equipment, weapons, ammunition, and munitions to developing nations. The sales serve both commercial and strategic purposes. Olvana is currently developing a laboratory complex to further research and development of military capabilities. The Olvana Defense Minister recently sealed a deal for an Olvanan arms factory to build a production and maintenance facility for Olvanan weapons in Belesia.
Nuclear
Olvana has a nuclear power program and possesses nuclear weapons. They currently have 11 nuclear power plants that produce approximately 3 percent of the nation’s power. All of the nuclear plants have been built in the past 20 years and are presumed to be safe. The country has not signed any nuclear non-proliferation or destruction treaties. Olvana is believed to possess approximately 500 nuclear warheads. There is an extensive underground network of tunnels throughout the country where the warheads and missiles are stored to protect them from attack from aircraft, artillery, and missiles.
Space
Olvana actively continues pursuit of a space program that supports the country's strategic vision. It currently has 23 satellites for communications and navigation purposes in orbit. They have been advancing their rocket program as delivery vehicles for their satellites and other space platforms. The Olvana space program also continues a program to develop an orbital space station for research and development.
Pollution
Olvana faces a wide range of pollution issues to include air pollution, ground water contamination, and pollution of lakes and rivers. Much of the pollution stems from the lack of environmental regulation and the industrial boom in the late 20th century. With the government running all the industry during that time there was little concern for the environment. Air pollution, especially in the major cities, is among the worst in the world. The use of coal to heat buildings and provide power has created a smog level that is the intolerable. The main pollutants from the industrial sector are from heavy metals (lead, mercury, chromium). Olvana has taken an aggressive stance on reducing the pollution throughout the country and has improved air quality by over 30% in the past 10 years. The government is actively enforcing antipollution and environmental regulations.