Difference between revisions of "Nyumba Infrastructure"
Allen.brian (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ">[[Africa|DATE Africa]] > [[Nyumba]] > '''{{PAGENAME}}''' ←You are here | + | <div style="font-size:0.9em; color:#333;" id="mw-breadcrumbs"> |
| + | [[Africa|DATE Africa]] > [[Nyumba]] > '''{{PAGENAME}}''' ←You are here | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| − | + | Nyumba is the least populated and least densely populated country in the region. The limited infrastructure is significantly degraded. Most of the population and development is concentrated along the Tana and Juba Rivers, and the Indian Ocean ports of Lamu and Kismaayo. Paved roads are limited to the main artery running from Moyale in the north to Isiolo on the Amari border, and a 150 km strip from Kismaayo running northeast to Jilib. | |
| − | + | Nyumba has the least developed infrastructure in the region. It is only partially connected to regional infrastructure networks. The exception is the northern portion of a transcontinental road corridor that connects southern Africa with the Red Sea. It depends entirely on imported electricity and refined petroleum. Despite its poverty and lack of development, in most years Nyumbans have access to sustainable water resources. | |
| − | == Major Cities and Urban Zones == | + | == Major Cities and Urban Zones == |
| + | Nyumba is predominantly a rural country with most development along the Tana River and Juba Rivers. | ||
| − | + | See Also: [[DATE Africa Regional Infrastructure#Construction Patterns|Regional Construction Patterns]] for a comparative summary. | |
| − | ' | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| + | |+Nyumba's Major Cities | ||
| + | !City | ||
| + | !Est. Pop. | ||
| + | (2017) | ||
| + | !Pop. Dens. | ||
| + | per km<sup>2</sup> | ||
| + | !UBD | ||
| + | !Rd | ||
| + | !Air | ||
| + | !Rail | ||
| + | !Sea | ||
| + | !Pwr. | ||
| + | !Wtr. | ||
| + | !Sew | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Kismaayo | ||
| + | |235,000 | ||
| + | |5,595 | ||
| + | |H- | ||
| + | |P | ||
| + | |Mo | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |Mo- | ||
| + | |Dg | ||
| + | |Dg | ||
| + | |Dg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Garissa | ||
| + | |119,696 | ||
| + | |1,361 | ||
| + | |M+ | ||
| + | |Mo | ||
| + | |Mo | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |Dv- | ||
| + | |Dv- | ||
| + | |Dv | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Lodwar | ||
| + | |55,006 | ||
| + | |3,039 | ||
| + | |L+ | ||
| + | |Mo- | ||
| + | |Mo | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |Dv- | ||
| + | |Dv | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Isiolo | ||
| + | |40,153 | ||
| + | |1,940 | ||
| + | |M+ | ||
| + | |Mo | ||
| + | |Mo | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |Dv- | ||
| + | |Dv- | ||
| + | |Dv | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Lamu | ||
| + | |21,736 | ||
| + | |3,105 | ||
| + | |M | ||
| + | |P | ||
| + | |Mo+ | ||
| + | |NE | ||
| + | |P+ | ||
| + | |Dv- | ||
| + | |Dv- | ||
| + | |Dv | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <small>''Legend (per TC-7-101): (UBD) urbanized building density, (L) low, (M) medium, (H) high, (P) primitive, (M) moderate, (C) complex, (NE) non-existent, (Dg) degraded, (Dv) developed''</small> | ||
| − | + | === '''Kismaayo''' === | |
| + | Nyumba’s capital city and principal port, Kismaayo, is located on the Indian Ocean coast. It sits on a low hilltop overlooking the port to the south. The city center has a moderate building density of dilapidated colonial mid-rise buildings surrounded by organized shantytown construction. | ||
| − | + | Beyond the dense random waterfront development, organized settlements are divided between directional grid and dense random construction patterns with few outward signs of affluent neighborhoods. Most residences are single story, densely packed dwellings with either concrete or dirt floors, mud walls, and corrugated metal roofing. Improved sanitation is mostly limited to public buildings and guesthouses. Electricity comes from one of two concessionaires using diesel generators and makeshift power lines. | |
| − | + | Kismaayo’s port has made it Nyumba’s main trading center. Livestock and charcoal are the main exports, and sugar is the main import. Commercial enterprises are mainly freight forwarding companies and a modest fishing fleet. | |
| − | + | The main commercial strip runs along the city’s primary road, most heavily developed on the west side between the city center and the airport. Kismaayo has a functional market, banks, internet connectivity, filling stations, restaurants, and hotels. Government building construction is similar to the Ziwan capital of Musoma. | |
| − | + | === '''Garissa''' === | |
| + | Garissa is the second largest city in Nyumba and borders Amari on the Tana River. Local government maintains close ties to Amari due to trade and a growing electrical power interchange. A 3 km2 quadrant in the northern section of the city is the most developed, bordered by the river valley to the west, and the main highway to the east. Less dense development continues beyond this quadrant. Spacious residential properties make up Garissa’s southern section, separated from quasi-dense random residences to the east by the city’s airport. | ||
| − | The | + | The main commercial strip runs for 4 km along the highway south of the city center. Besides livestock and agricultural facilities, the area is also home to many government and educational institutions. |
| − | + | === '''Lodwar''' === | |
| + | Lodwar is the main city in remote northwest Nyumba. It sits on the junction of the A1 highway linking north central Africa with points south and the main road to the western shore of Lake Turkana. Lodwar is a key node in the planned LAPEX project. The city straddles the Turkwel River with most development on the north side of the river. A dry riverbed confluence forms Lodwar’s north and east boundaries. | ||
| − | + | Regional government, Lake Turkana tourism and support services make up the bulk of Lodwar’s development. Basic health, education, banking, and hospitality facilities are available. The city 0.6 km2 city center surrounds the road junction in a dense random construction pattern. | |
| − | + | === '''Isiolo''' === | |
| + | Isiolo sits 10 km north of the Amari border on the main north-south Trans-African Highway along the east bank of the Isiolo River. 30,000 square kilometers of government and private nature reserve surrounds the city. It is also the proposed site of a significant LAPEX oil refinery/terminal complex and rail yard. | ||
| − | + | The city center is a .05 km2 closed block urban core straddling the main road in the city center. Most multi-story buildings are hotels or office buildings and are less than four levels. A 1.5 km. commercial strip runs along the highway just south of the core. The rest of Isiolo’s development is randomly arranged to the west of the core and commercial strip. It extends approximately on half kilometer. | |
| − | + | There are two significant compounds within the city limits. A 46 acre retreat-style complex sits east of the commercial strip between the highway and the town’s unpaved airport. A 500 acre security cantonment is 2.5 km. east of the city center. Samburu, the largest of the nature reserves to the northwest, has two 2,500 ft. airstrips, the southerly being paved. | |
| − | + | === '''Lamu''' === | |
| + | Lamu is a small port city on the southern coast of Nyumba, 75 km. by road to the Amari border town of Garsen and 40 km. by air and sea to the coastal boundary. The main population center is on the eastern side of a 50 km2 island in the center of a coastal wetland archipelago. Lamu Island has a modest fishing industry, and exclusive eco-tourist enterprises. | ||
| − | + | Currently, most of the city’s 21,000 inhabitants live in the old city of Lamu, a .65 km2 dense random complex of narrow multistory buildings constructed in the 19th century. Lamu prohibits motor vehicles because of the city’s narrow streets and historic status. An equally dense, but less restricted quarter is south of the historic district. The densely populated fishing settlement of Shela sits on the southeast end of the island. The rest of the island is sparsely populated. | |
| − | + | Lamu’s critical feature is the deep-water natural harbor of Manda Bay, and the 460 km2 planned development on the mainland peninsula directly north of Lamu Island. It features rail and pipeline terminals connecting directly to a 30+ berth marine terminal. A refinery and power plant would occupy the northern tract, and a naval base in the southern tract. The entire project has received international notoriety due to its ambitious size and the environmental sensitivity of the location. (<nowiki>https://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/features/2013/10/mega-port-threatens-sink-sudan-2013101371736417765.html</nowiki>) <nowiki>https://constructionreviewonline.com/2017/06/dredging-work-on-lamu-first-berth-to-be-completed-in-2018/</nowiki> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''''Image Gallery''''' | '''''Image Gallery''''' | ||
<gallery mode="packed-hover" heights="180"> | <gallery mode="packed-hover" heights="180"> | ||
| − | File: | + | File:KismaayoStreetandTaxi.jpg| |
| − | File: | + | File:NyumbaCharcoal.jpg| |
| − | File: | + | File:Lamu Harbor.jpg| |
| − | File: | + | File:LokicharRoadConst.jpg| |
| − | File: | + | File:75M42VZ 49D8VBHQK.jpg| |
| − | File: | + | File:Village.jpg| |
| − | File: | + | File:Kismaayoroad.jpg| |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Utilities == | == Utilities == | ||
| Line 67: | Line 137: | ||
=== Electricity Generation and Transmission === | === Electricity Generation and Transmission === | ||
| − | + | Nyumba’s sole operational power plant is a wind farm in the Lake Turkana region generating 300 Mw. Two more wind farms with a combined 490 Mw are under construction as is a 960 Mw coal fired plant near Lamu. Most of the transmission grid is located in southern Nyumba with extensive Amari links in Lamu and the border towns of Garissa, Isiolo, and Lodwar. | |
| − | + | [[File:75M3LQ0 1B8C2T4T3.jpg|thumb|Camels at Nyumba Watering Hole]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
=== Water === | === Water === | ||
See also: [[Physical Environment: Ziwa]] | See also: [[Physical Environment: Ziwa]] | ||
| − | + | Despite cyclical droughts affecting the larger region, Nyumba’s main sources of water are the Tana, Juba, and Shabelle Rivers. They all drain to the Indian Ocean. These river valleys also support limited agricultural development confined to narrow strips along the waterways. Manmade irrigation is minimal. The alkaline Lake Turkana in north central Nyumba is the world’s largest permanent desert lake, fed by the Omo River to the north. Upstream dam projects threaten water levels with environmental groups estimating a fifty percent reduction in surface area and volume by mid-century. | |
| − | + | There is little census data available for Nyumba. A limited number of standpipes are available to urban inhabitants, and most of the rural population depends on watering holes or rivers for water. UNICEF is building smaller, decentralized water and sanitation systems. The hope is that these will be easier to maintain than earlier centralized systems still common in developed countries. | |
| − | == | + | === Sanitation === |
| + | See also: [[DATE Africa Regional Infrastructure|Date Africa Regional Infrastructure]] | ||
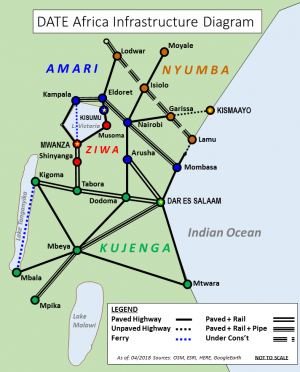
| + | [[File:Africa Infrastructure Schematicv2.png|thumb|Regional Transportation Architecture]] | ||
| + | == Transportation Architecture == | ||
=== Roads === | === Roads === | ||
| − | + | Nyumba has the least developed and maintained road network in the region. The north and central regions are connected with their neighbors to the north and south, but eastern and coastal Nyumba are more remote. The single paved regional highway is only paved west of Garissa. Little of the eastern road network is paved and many communities are only connected by tertiary roads or tracks. Coastal roads are also unreliable. | |
| − | + | International investors, both private and public, view the lack of highway development as an opportunity. Besides the LAPEX development initiatives, the government plans to improve the coastal highway and complete of the Kismaayo-Garissa link. These projects would improve access to Nairobi and points south, and enable a direct route between Kismaayo and the Lamu megaport. | |
=== Rail === | === Rail === | ||
| − | + | Nyumba has no active railroads. A planned SGR railroad would connect northwest Nyumba with Lamu as part of the LAPEX initiative. Another would connecting Isiolo with Moyale following the general path of the Trans-Africa Highway. | |
=== Aviation === | === Aviation === | ||
| − | + | Nyumba’s only international airport is Kismaayo International (HCMK). Wajir Airport (HKWJ) in central Nyumba is the only other airport with a paved runway over 5,000 ft. There are 18 more serviceable airfields with runway lengths between 5,000 and 2,450 ft. | |
| + | |||
| + | Nyumba has no national air carrier. Intercontinental and regional carriers have weekly flights to Kismaayo via Nairobi. Occasional intercontinental charter flights also make use of Kismaayo and Wajir. Fixed based operator services are limited to basic fuel and provisioning. Ziwan or Amari operators provide most charter service in Nyumba. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Facilities. See attached link for specific runway data. | ||
| − | + | === Maritime Seaports === | |
| − | + | Nyumba has only 2 seaports located along Africa’s east coast. There is only 1 Kujenga port that average more than 1 million tons of cargo throughput annually. There is no data outlining the annual cargo throughput of the Port of Kismayo and the port can’t accommodate a Military Sea Lift (MSC) Commands Large, Medium-Speed Roll-on/Roll-off (LMSR). The Port of Kismayo, is Nyumbia’s sole port and is situated on the southern coast of Nyumbia . The Port of Kismayo was built in 1966 for the purpose of exporting bananas and other small products and importing other agricultural machineries as well as other goods, as the road between Mogadishu and Kismayu was only accessible during the dry season therefore, the port was to cover the needs of the lower Jubba. After more than 20 years the port has not been maintained. | |
| + | [[File:The Port of Kismayo.png|center|'''<big>The Port of Kismayo</big>'''|frame]] | ||
| − | + | Kismayo's large docks are situated on a peninsula on the Indian Ocean coast. Formerly one of the Bajuni Islands, the peninsula was subsequently connected by a narrow causeway when the modern Port of Kismayo was built in 1964 with U.S. assistance. The port served as a base for the Nyumbia’s Navy as well as the Soviet Navy after the military coup in Nyumbia in 1969. Nyumbia and the United States jointly refurbished the port in 1984 after significant wear to the 2,070-foot-long (630 m) four-berth, marginal wharf at the harbor required major renovations to maintain operations. | |
| + | |||
| + | . | ||
| + | [[File:Nyumba port update.png|thumb|1159x1159px]] | ||
| + | . | ||
| + | |||
| + | . | ||
| + | |||
| + | . | ||
| + | |||
| + | . | ||
| + | |||
| + | . | ||
| + | |||
| + | . | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Petroleum Pipeline and Storage === | ||
| + | Nyumba has no pipeline systems. Kismaayo and Wajir have limited AVGAS and Jet-A storage to support regularly scheduled air service. Diesel and gasoline stocks are limited to retail storage at service stations along the major highways. Tanker trucks supply these stations. Kismaayo has a modest tank terminal to support product deliveries at the port. | ||
== Pollution == | == Pollution == | ||
| − | + | Most of Nyumba’s water pollution comes from raw sewage and animal processing entering the watersheds. Lake Turkana, the largest lake in Nyumba, is shrinking due to upstream hydroelectric power and irrigation development from neighboring countries to the north. (link to Nyumba water section) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The Lamu coal-fired power plant project poses the most significant air pollution concern. This development pits local economic development against local and international environmental groups and is the main reason the project remains suspended. | |
[[Category:DATE]] | [[Category:DATE]] | ||
[[Category:Africa]] | [[Category:Africa]] | ||
[[Category:Ziwa]] | [[Category:Ziwa]] | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:45, 2 July 2020
Nyumba is the least populated and least densely populated country in the region. The limited infrastructure is significantly degraded. Most of the population and development is concentrated along the Tana and Juba Rivers, and the Indian Ocean ports of Lamu and Kismaayo. Paved roads are limited to the main artery running from Moyale in the north to Isiolo on the Amari border, and a 150 km strip from Kismaayo running northeast to Jilib.
Nyumba has the least developed infrastructure in the region. It is only partially connected to regional infrastructure networks. The exception is the northern portion of a transcontinental road corridor that connects southern Africa with the Red Sea. It depends entirely on imported electricity and refined petroleum. Despite its poverty and lack of development, in most years Nyumbans have access to sustainable water resources.
Contents
Major Cities and Urban Zones
Nyumba is predominantly a rural country with most development along the Tana River and Juba Rivers.
See Also: Regional Construction Patterns for a comparative summary.
| City | Est. Pop.
(2017) |
Pop. Dens.
per km2 |
UBD | Rd | Air | Rail | Sea | Pwr. | Wtr. | Sew |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kismaayo | 235,000 | 5,595 | H- | P | Mo | NE | Mo- | Dg | Dg | Dg |
| Garissa | 119,696 | 1,361 | M+ | Mo | Mo | NE | NE | Dv- | Dv- | Dv |
| Lodwar | 55,006 | 3,039 | L+ | Mo- | Mo | NE | NE | NE | Dv- | Dv |
| Isiolo | 40,153 | 1,940 | M+ | Mo | Mo | NE | NE | Dv- | Dv- | Dv |
| Lamu | 21,736 | 3,105 | M | P | Mo+ | NE | P+ | Dv- | Dv- | Dv |
Legend (per TC-7-101): (UBD) urbanized building density, (L) low, (M) medium, (H) high, (P) primitive, (M) moderate, (C) complex, (NE) non-existent, (Dg) degraded, (Dv) developed
Kismaayo
Nyumba’s capital city and principal port, Kismaayo, is located on the Indian Ocean coast. It sits on a low hilltop overlooking the port to the south. The city center has a moderate building density of dilapidated colonial mid-rise buildings surrounded by organized shantytown construction.
Beyond the dense random waterfront development, organized settlements are divided between directional grid and dense random construction patterns with few outward signs of affluent neighborhoods. Most residences are single story, densely packed dwellings with either concrete or dirt floors, mud walls, and corrugated metal roofing. Improved sanitation is mostly limited to public buildings and guesthouses. Electricity comes from one of two concessionaires using diesel generators and makeshift power lines.
Kismaayo’s port has made it Nyumba’s main trading center. Livestock and charcoal are the main exports, and sugar is the main import. Commercial enterprises are mainly freight forwarding companies and a modest fishing fleet.
The main commercial strip runs along the city’s primary road, most heavily developed on the west side between the city center and the airport. Kismaayo has a functional market, banks, internet connectivity, filling stations, restaurants, and hotels. Government building construction is similar to the Ziwan capital of Musoma.
Garissa
Garissa is the second largest city in Nyumba and borders Amari on the Tana River. Local government maintains close ties to Amari due to trade and a growing electrical power interchange. A 3 km2 quadrant in the northern section of the city is the most developed, bordered by the river valley to the west, and the main highway to the east. Less dense development continues beyond this quadrant. Spacious residential properties make up Garissa’s southern section, separated from quasi-dense random residences to the east by the city’s airport.
The main commercial strip runs for 4 km along the highway south of the city center. Besides livestock and agricultural facilities, the area is also home to many government and educational institutions.
Lodwar
Lodwar is the main city in remote northwest Nyumba. It sits on the junction of the A1 highway linking north central Africa with points south and the main road to the western shore of Lake Turkana. Lodwar is a key node in the planned LAPEX project. The city straddles the Turkwel River with most development on the north side of the river. A dry riverbed confluence forms Lodwar’s north and east boundaries.
Regional government, Lake Turkana tourism and support services make up the bulk of Lodwar’s development. Basic health, education, banking, and hospitality facilities are available. The city 0.6 km2 city center surrounds the road junction in a dense random construction pattern.
Isiolo
Isiolo sits 10 km north of the Amari border on the main north-south Trans-African Highway along the east bank of the Isiolo River. 30,000 square kilometers of government and private nature reserve surrounds the city. It is also the proposed site of a significant LAPEX oil refinery/terminal complex and rail yard.
The city center is a .05 km2 closed block urban core straddling the main road in the city center. Most multi-story buildings are hotels or office buildings and are less than four levels. A 1.5 km. commercial strip runs along the highway just south of the core. The rest of Isiolo’s development is randomly arranged to the west of the core and commercial strip. It extends approximately on half kilometer.
There are two significant compounds within the city limits. A 46 acre retreat-style complex sits east of the commercial strip between the highway and the town’s unpaved airport. A 500 acre security cantonment is 2.5 km. east of the city center. Samburu, the largest of the nature reserves to the northwest, has two 2,500 ft. airstrips, the southerly being paved.
Lamu
Lamu is a small port city on the southern coast of Nyumba, 75 km. by road to the Amari border town of Garsen and 40 km. by air and sea to the coastal boundary. The main population center is on the eastern side of a 50 km2 island in the center of a coastal wetland archipelago. Lamu Island has a modest fishing industry, and exclusive eco-tourist enterprises.
Currently, most of the city’s 21,000 inhabitants live in the old city of Lamu, a .65 km2 dense random complex of narrow multistory buildings constructed in the 19th century. Lamu prohibits motor vehicles because of the city’s narrow streets and historic status. An equally dense, but less restricted quarter is south of the historic district. The densely populated fishing settlement of Shela sits on the southeast end of the island. The rest of the island is sparsely populated.
Lamu’s critical feature is the deep-water natural harbor of Manda Bay, and the 460 km2 planned development on the mainland peninsula directly north of Lamu Island. It features rail and pipeline terminals connecting directly to a 30+ berth marine terminal. A refinery and power plant would occupy the northern tract, and a naval base in the southern tract. The entire project has received international notoriety due to its ambitious size and the environmental sensitivity of the location. (https://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/features/2013/10/mega-port-threatens-sink-sudan-2013101371736417765.html) https://constructionreviewonline.com/2017/06/dredging-work-on-lamu-first-berth-to-be-completed-in-2018/
Image Gallery
Utilities
Electricity Generation and Transmission
Nyumba’s sole operational power plant is a wind farm in the Lake Turkana region generating 300 Mw. Two more wind farms with a combined 490 Mw are under construction as is a 960 Mw coal fired plant near Lamu. Most of the transmission grid is located in southern Nyumba with extensive Amari links in Lamu and the border towns of Garissa, Isiolo, and Lodwar.
Water
See also: Physical Environment: Ziwa
Despite cyclical droughts affecting the larger region, Nyumba’s main sources of water are the Tana, Juba, and Shabelle Rivers. They all drain to the Indian Ocean. These river valleys also support limited agricultural development confined to narrow strips along the waterways. Manmade irrigation is minimal. The alkaline Lake Turkana in north central Nyumba is the world’s largest permanent desert lake, fed by the Omo River to the north. Upstream dam projects threaten water levels with environmental groups estimating a fifty percent reduction in surface area and volume by mid-century.
There is little census data available for Nyumba. A limited number of standpipes are available to urban inhabitants, and most of the rural population depends on watering holes or rivers for water. UNICEF is building smaller, decentralized water and sanitation systems. The hope is that these will be easier to maintain than earlier centralized systems still common in developed countries.
Sanitation
See also: Date Africa Regional Infrastructure
Transportation Architecture
Roads
Nyumba has the least developed and maintained road network in the region. The north and central regions are connected with their neighbors to the north and south, but eastern and coastal Nyumba are more remote. The single paved regional highway is only paved west of Garissa. Little of the eastern road network is paved and many communities are only connected by tertiary roads or tracks. Coastal roads are also unreliable.
International investors, both private and public, view the lack of highway development as an opportunity. Besides the LAPEX development initiatives, the government plans to improve the coastal highway and complete of the Kismaayo-Garissa link. These projects would improve access to Nairobi and points south, and enable a direct route between Kismaayo and the Lamu megaport.
Rail
Nyumba has no active railroads. A planned SGR railroad would connect northwest Nyumba with Lamu as part of the LAPEX initiative. Another would connecting Isiolo with Moyale following the general path of the Trans-Africa Highway.
Aviation
Nyumba’s only international airport is Kismaayo International (HCMK). Wajir Airport (HKWJ) in central Nyumba is the only other airport with a paved runway over 5,000 ft. There are 18 more serviceable airfields with runway lengths between 5,000 and 2,450 ft.
Nyumba has no national air carrier. Intercontinental and regional carriers have weekly flights to Kismaayo via Nairobi. Occasional intercontinental charter flights also make use of Kismaayo and Wajir. Fixed based operator services are limited to basic fuel and provisioning. Ziwan or Amari operators provide most charter service in Nyumba.
Facilities. See attached link for specific runway data.
Maritime Seaports
Nyumba has only 2 seaports located along Africa’s east coast. There is only 1 Kujenga port that average more than 1 million tons of cargo throughput annually. There is no data outlining the annual cargo throughput of the Port of Kismayo and the port can’t accommodate a Military Sea Lift (MSC) Commands Large, Medium-Speed Roll-on/Roll-off (LMSR). The Port of Kismayo, is Nyumbia’s sole port and is situated on the southern coast of Nyumbia . The Port of Kismayo was built in 1966 for the purpose of exporting bananas and other small products and importing other agricultural machineries as well as other goods, as the road between Mogadishu and Kismayu was only accessible during the dry season therefore, the port was to cover the needs of the lower Jubba. After more than 20 years the port has not been maintained.
Kismayo's large docks are situated on a peninsula on the Indian Ocean coast. Formerly one of the Bajuni Islands, the peninsula was subsequently connected by a narrow causeway when the modern Port of Kismayo was built in 1964 with U.S. assistance. The port served as a base for the Nyumbia’s Navy as well as the Soviet Navy after the military coup in Nyumbia in 1969. Nyumbia and the United States jointly refurbished the port in 1984 after significant wear to the 2,070-foot-long (630 m) four-berth, marginal wharf at the harbor required major renovations to maintain operations.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Petroleum Pipeline and Storage
Nyumba has no pipeline systems. Kismaayo and Wajir have limited AVGAS and Jet-A storage to support regularly scheduled air service. Diesel and gasoline stocks are limited to retail storage at service stations along the major highways. Tanker trucks supply these stations. Kismaayo has a modest tank terminal to support product deliveries at the port.
Pollution
Most of Nyumba’s water pollution comes from raw sewage and animal processing entering the watersheds. Lake Turkana, the largest lake in Nyumba, is shrinking due to upstream hydroelectric power and irrigation development from neighboring countries to the north. (link to Nyumba water section)
The Lamu coal-fired power plant project poses the most significant air pollution concern. This development pits local economic development against local and international environmental groups and is the main reason the project remains suspended.