Difference between revisions of "Physical Environment: Kujenga"
Hunt.james (talk | contribs) m (Added banner per A.Williams) |
Allen.brian (talk | contribs) m (initial content update) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
== Bodies of Water == | == Bodies of Water == | ||
| − | + | Kujenga has the longest Indian Ocean coastline of the DATE Africa countries. It also has the most inland water area, dominated by the great lakes of the African Rift Valleys. From the south, these include Lakes Nyassa (Malawi), Tanganyika, and Victoria. Significant, but lesser freshwater lakes dominate the south, and the alkali Lakes Eyasi and Natron form Kujenga's border with Ziwa. | |
| + | |||
| + | The 830 km Ruvuma River forms the southern boundary of Kujenga, flowing to the Indian Ocean. The much smaller Umba River forms the Amari-Kujenga border, also terminating at the Indian Ocean. | ||
== Mobility Classification == | == Mobility Classification == | ||
| − | + | Similar to Amari, Kujenga is characterized by relatively broad a coastal plain gradually rising to a plateau as you travel westward. This corridor is relatively unrestricted all the way to the western frontier at the Kigoma on Lake Tanganyika. Terrain remains unrestricted on a northward branch of this corridor, all the way to the southern shore of Lake Victoria in Ziwa. Not surprisingly, the DARGOMA rail and road corridors follow this route. | |
| + | |||
| + | Access to the southwestern corner of Kujenga becomes more restricted as the plateau gives way to highlands at the convergence of the East and West Rift Valleys around Mbeya. Travel further west from Mbeya is further hampered by rougher terrain and denser vegetation and wetlands. A well-established road and rail corridor runs southwest from Dar Es Salaam, through Mbeya past Kujenga's southwestern frontier to Lusaka with further connection to southern African cities. | ||
== Natural Hazards == | == Natural Hazards == | ||
| − | + | Of the hazards listed in the regional assessment, the water and wetland obstacles in far eastern Kujenga are the most challenging. The Kujengan Bush Militia and other armed groups take advantage of these obstacles when selecting bases and areas of operation. | |
== Subterranean Environment == | == Subterranean Environment == | ||
Revision as of 21:05, 11 June 2018
DATE Africa > Kujenga > Physical Environment: Kujenga ←You are here
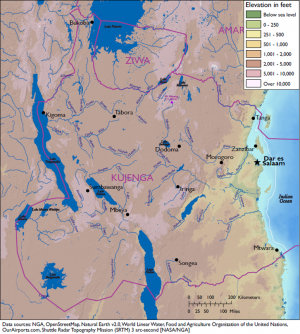
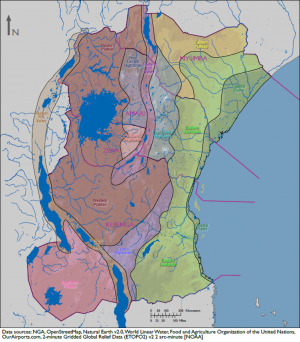
Kujenga is a large country located in central eastern Africa and is roughly rectangular in shape. It borders one major body of water: the Indian Ocean and encompasses three others, Lake Victoria, Lake Malawi, Lake Tanganika. The country’s terrain varies from a significant rift valley in the central region, high mountains and arid desert lowlands, as well as coastal plains, with climates ranging from in the east, tropical to semiarid; warm desert in the west; and humid near the coast.
Contents
Table of Physical Environment Data
| Measure | Data | Remarks |
| Total Area (sq miles) | 390,810 | Includes inland water |
| Land Area (sq miles) | 364,374 | Excludes inland water |
| Inland Water (sq miles) | 26,437 | Includes Lake Tanganyika, Lake Niassa, Lake Bangweulu, and Lake Rukwa |
| Inland Border (miles) | 3,073 | Amari (517), Ziwa (487) |
| Coastline (miles) | 2,834 | Indian Ocean (1,570), Lake Victoria (315), Lake Niassa (439), Lake Tanganyika (511) |
| Highest Elevation (ft) | 11,220 | Mt Hanang |
| Lowest Elevation (ft) | 0 | Sea level |
| Arable (cultivated) Land (%) | ||
| Permanent Crops (%) | ||
| Permanent Pasture (%) | ||
| Irrigated Land (%) | ||
| Forested Land (%) | ||
| Urban Area (%) |
Terrain
Kujenga’s area is 390,810 square miles in the eastern part of central Africa. It shares 3,073 miles of border with several different countries, including Amari and Ziwa to the north, and four major bodies of water—the Indian Ocean, Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika, and Lake Niassa. The country’s varied terrain includes mountainous highlands, high plateaus, deep valleys, lowland plains, and sandy beaches.
Border Disputes
The Tanga region, a small triangle of land defined by the far southeastern Amari border, the Pangani River, and the Indian Ocean formally belongs to Kujenga. However, its populace identifies with Amari, and wishes to join that country. Though the land is not disputed per se, the situation occasionally leads to political tensions between these two neighbors. Armed outbreaks occur episodically, primarily between the local populace and Kujengan security forces, though Amarian security forces have also been involved.
Bodies of Water
Kujenga has the longest Indian Ocean coastline of the DATE Africa countries. It also has the most inland water area, dominated by the great lakes of the African Rift Valleys. From the south, these include Lakes Nyassa (Malawi), Tanganyika, and Victoria. Significant, but lesser freshwater lakes dominate the south, and the alkali Lakes Eyasi and Natron form Kujenga's border with Ziwa.
The 830 km Ruvuma River forms the southern boundary of Kujenga, flowing to the Indian Ocean. The much smaller Umba River forms the Amari-Kujenga border, also terminating at the Indian Ocean.
Mobility Classification
Similar to Amari, Kujenga is characterized by relatively broad a coastal plain gradually rising to a plateau as you travel westward. This corridor is relatively unrestricted all the way to the western frontier at the Kigoma on Lake Tanganyika. Terrain remains unrestricted on a northward branch of this corridor, all the way to the southern shore of Lake Victoria in Ziwa. Not surprisingly, the DARGOMA rail and road corridors follow this route.
Access to the southwestern corner of Kujenga becomes more restricted as the plateau gives way to highlands at the convergence of the East and West Rift Valleys around Mbeya. Travel further west from Mbeya is further hampered by rougher terrain and denser vegetation and wetlands. A well-established road and rail corridor runs southwest from Dar Es Salaam, through Mbeya past Kujenga's southwestern frontier to Lusaka with further connection to southern African cities.
Natural Hazards
Of the hazards listed in the regional assessment, the water and wetland obstacles in far eastern Kujenga are the most challenging. The Kujengan Bush Militia and other armed groups take advantage of these obstacles when selecting bases and areas of operation.
Subterranean Environment
To be published
Vegetation
To be published
Agriculture
To be published
Livestock and Wildlife
To be published
Climate and Weather
To be published
Seasons
To be published
Precipitation
To be published
Temperature-Heat Index
To be published
Temperature-Wind Chill Index
To be published
Relative Humidity
To be published
Wind
To be published
Summary
To be published
| DATE Africa Quick Links . | |
|---|---|
| Amari | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Kujenga | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Nyumba | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Ziwa | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Other | Non-State Threat Actors and Conditions • Criminal Activity • DATE Map References • Using The DATE |