Difference between revisions of "Physical Environment: Kujenga"
(Added terrain and terrain regions maps (2 total)) (Tag: Visual edit) |
m (adjusted spacing) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
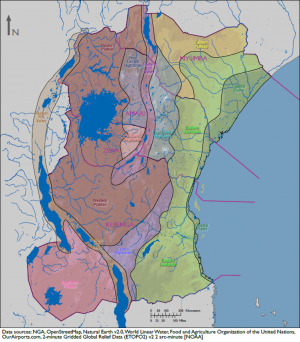
[[Africa|DATE Africa]] > [[Kujenga]] > '''{{PAGENAME}}''' ←You are here | [[Africa|DATE Africa]] > [[Kujenga]] > '''{{PAGENAME}}''' ←You are here | ||
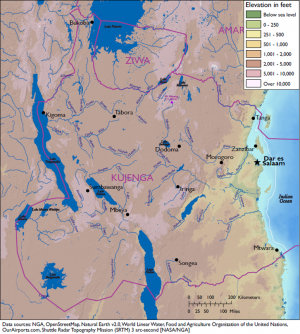
[[File:Kujenga terrain map.PNG|thumb|Physical Map of Kujenga]] | [[File:Kujenga terrain map.PNG|thumb|Physical Map of Kujenga]] | ||
| + | |||
Nyumba is a moderately large country located in eastern Africa. It borders one major body of water: the Indian Ocean and encompasses two others, Lake Turkana and Lake Logipi. The country’s terrain varies from significant a rift valley, high mountains and arid desert lowlands, as well as coastal plains, with climates ranging from east, tropical to semiarid and in the west, warm desert and arid and humid near the coast. | Nyumba is a moderately large country located in eastern Africa. It borders one major body of water: the Indian Ocean and encompasses two others, Lake Turkana and Lake Logipi. The country’s terrain varies from significant a rift valley, high mountains and arid desert lowlands, as well as coastal plains, with climates ranging from east, tropical to semiarid and in the west, warm desert and arid and humid near the coast. | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 24 April 2018
DATE Africa > Kujenga > Physical Environment: Kujenga ←You are here
Nyumba is a moderately large country located in eastern Africa. It borders one major body of water: the Indian Ocean and encompasses two others, Lake Turkana and Lake Logipi. The country’s terrain varies from significant a rift valley, high mountains and arid desert lowlands, as well as coastal plains, with climates ranging from east, tropical to semiarid and in the west, warm desert and arid and humid near the coast.
Contents
Table of Physical Environment Data
Terrain
Amari’s land area is 196,575 square miles in the eastern part of central Africa. It shares 3,158 miles of border with several different countries, including Kujenga and Ziwa to the south and Nyumba to the north, and two major bodies of water—the Indian Ocean and Lake Victoria. The country’s varied terrain includes mountainous highlands, high plateaus, deep valleys, lowland plains, and sandy beaches.
Border Disputes
The Tanga region, a small triangle of land defined by the far southeastern Amari border, the Pangani River, and the Indian Ocean formally belongs to Kujenga. However, its populace identifies with Amari, and wishes to join that country. Though the land is not disputed per se, the situation occasionally leads to political tensions between these two neighbors. Armed outbreaks occur episodically, primarily between the local populace and Kujengan security forces, though Amarian security forces have also been involved.
Bodies of Water
Amari’s most prominent bodies of water are the Indian Ocean to the east and Lake Victoria in the southwest. The country shares maritime borders on the Indian Ocean with Nyumba and Kujenga, and operates a major deepwater port at Mombasa. The ocean is a major source of fish, both for internal consumption and for export, which occasionally leads to quarrels between Amari and its neighbors. Recent discoveries of natural gas in Amarian waters could be another source of conflict.
Mobility Classification
Movement in Amari is less restricted in the western plateau and lowland plains than in other regions. Steep escarpments separate the two Rift Valleys from their surrounding terrain; both valleys contain active volcanoes. Glaciers exist on Amari’s highest peaks, while forests and mangroves hamper movement along the coastal plains. Mountainous terrain and rough roads make it hard to transport troops and equipment overland. Multiple rivers and streams—especially in the western half to the country—also challenge mechanized and motorized movement. Roads can become flooded during the rainy season, making them impassable. These rains also greatly affect visibility for reconnaissance and air operations. Foot movement is also limited in the central highlands by the negative effects of the high altitudes.
Natural Hazards
Both natural disasters and manmade hazards exist in Amari. Natural disasters include flooding, earthquakes, limited volcanic activity in the Rift Valleys, landslides, windstorms, and hailstorms. Frequent droughts, including one ongoing for the past two years, can lead to famine. Violent thunderstorms with gusty winds are common on and around Lake Victoria. Water pollution is an issue, caused by urban waste, industrial waste, and contamination by pesticides and fertilizer. Overharvesting of trees for fuel led to significant deforestation and in turn soil erosion and desertification, especially in the eastern lowlands. Unexploded ordnance, including landmines, can be found in previous conflict zones. Dangerous indigenous wildlife include disease-carrying mosquitoes and tsetse flies, as well as more traditional threats: big cats (e.g., lions), crocodiles, elephants, gorillas, hippopotamuses, hyenas, rhinoceroses, warthogs, and wild dogs.
Subterranean Environment
The Amarian government has developed some underground facilities (UGFs), including structures to protect vital space program assets, bunkers for ammunition, and underground/hardened command posts. Subterranean systems used by criminal actors consist primarily of tunnels located on main smuggling routes, usually crossing the Amari-Kujenga border east of Lake Victoria. It is relatively easy to cross international borders in the region without detection, so tunnels are minimal in number and concentrated along routes more frequently patrolled by government forces. Insurgent use of such systems is minimal except in and around the Tanga region of Kujenga, where tunnels and underground rooms are used to avoid detection by local authorities. Natural caves are found throughout the country and in the Tanga region, and are used by criminals, insurgents, and local citizens alike.
Vegetation
Vegetation in Amari varies by topographical region. The Western Rift Valley and most of the western plateau consist primarily of savanna, with some forests in the swampy areas of the far southwest. The central highlands and Eastern Rift Valley contain most of the country’s forests, giving way to savanna in the far north and the east. The highest elevations are host to glaciers. The eastern lowlands are primarily grassland or desert scrub. The coastal plains have both grasslands and forested areas; mangrove forests grow on the coastline. Trees found in the country include both deciduous and evergreen, including species such as acacia, bamboo, baobob, cacti, candelabra, cedar, euphorbia, giant lobelia, groundsel, heath, miombo, papyrus, and podo.
Agriculture
Amarian agriculture employs 60% of the labor force full-time and an additional 15% part-time, producing 30% of the national GDP. The western region plays a very important role in this sector. Over one-third of Amari’s land is arable. Most farming takes place in the highlands or on the western plateau; much of the remainder of the country is either used for pasture or covered with forests or scrub vegetation. Due to reasonable rainfall, most irrigation in the country occurs in the drier eastern region. Crops produced in Amari include bananas, beans, beets, cabbages, carrots, cashews, cassava, citrus fruit, cocoa, coconut, coffee, corn, cotton, flowers, fruit, groundnuts, khale, legumes, mango, millet, oats, onions, palms (oil), peppers, pineapple, plantains, potatoes, pyrethrum, rice, sisal, sorghum, soybeans, sugarcane, sweet potato, tea, tobacco, tomatoes, turnips, vegetables, and wheat. Of these, cashews, coffee, cotton, cut flowers, pyrethrum, sisal, and tea are exported. Despite the large agricultural economy, the country does not grow enough cereal grains to feed its populace.
Livestock and Wildlife
Amarians have considerable livestock, especially in the drier regions where crop cultivation is more difficult. Common domesticated animals include bees, cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, and poultry. The country also boasts multiple types of wildlife, including aardvark, African buffalo, numerous different kinds of antelope, several species of big cat (cheetah, leopard, lion, wildcat), bush baby, crocodile, elephant, giraffe, hippopotamus, hyena, hyrax, mongoose, many types of primate (baboon, chimpanzee, gorilla, monkey), rhinoceros, warthog, wild dog, and zebra. While some of these species are only found in national parks and game reserves in Amari, others are more widespread. Many of these species are endangered and protected by Amarian law. Poaching is a continuing problem, with elephants and rhinoceroses being the most common targets. A couple of Amari’s game reserves are shared by Nyumba to the north and at times have been a source of contention because of the lack of national security forces in the parks, ivory smuggling, big game poaching, and drug trafficking occur through the border preserves.
Climate and Weather
Amari has a widely varied climate depending on location and altitude. The Western Rift Valley and western plateau experience a tropical wet and dry climate defined by rainy and dry seasons. The central highlands and Eastern Rift Valley are temperate (highland climate), with the highest peaks experiencing a sub-alpine climate. The far-eastern central highlands and the eastern lowlands are primarily semiarid. The coastal plains are tropical, with high temperatures and humidity throughout the year.
Seasons
Amari’s seasons center around the long rains and the short rains, which alternate with two distinct dry seasons. Most of the country experiences the long rains from approximately March through May, the short rains during September through December, and intervening dry seasons in June through August and January through February. In the central highlands, the two rains merge into one long rainy season from March through December, with a single dry season during January through March. The hottest months are January through March, while the coolest are July through August. Temperatures usually vary more from day to night than from season to season.
Precipitation
Precipitation in Amari varies primarily by season and latitude. Though usually taking the form of rain, snow is possible at extremely high elevations. Precipitation generally increases from north to south and with altitude. Most of the country receives 40–60 inches of precipitation per year, with some areas in the two Rift Valleys and around Lake Victoria receiving 60–80 inches. The eastern lowlands are by far the driest regions of the country, receiving only 10-40 inches annually, while the coastal plains receive 40–80 inches.
Temperature-Heat Index
Monthly average high temperatures in Amari vary with elevation. Most of the country enjoys highs between 70–85°F, with the extreme elevations—above 8,000 feet—being cooler than this. Average highs in the eastern lowlands, the coastal plains, and the far north are hotter, ranging from 80–100°F. The combination of high temperatures and moderate to high relative humidity can quickly lead to both dehydration and heat exhaustion in the regions with lower altitudes.
Temperature-Wind Chill Index
Monthly average low temperatures in the highlands and plateau fall in the 40–55°F range, though lower temperatures can occur. The lowlands are warmer than this, while elevations over 8,000 feet may experience sub-zero temperatures and snow. The highest peaks in the country possesses a permanent snow cap. Cold and wind chill will not be an issue in the lower elevations, but can affect troops operating in the highlands.
Relative Humidity
Relative humidity in Amari is moderate to high in most regions. Average annual humidity in the Western Rift Valley and western plateau usually ranges from 65–80%, with level in the north and east being lower. Levels in the central highlands and Eastern Rift Valley average 55–70%, with higher altitudes experiencing higher relative humidity and vice versa. Averages in the eastern lowlands are also 55–70%, while those in the coastal plains are 65–80%.
Wind
Wind patterns change with the seasons in Amari and are associated with the dry seasons. The Kuzi monsoon winds blow from the southeast and peaks during the months of June through August. The winds then shift to the gentler northeast Kaskazi, which peak from December through March. Average wind speeds are less than 15 mph throughout most of the country. Though calmer when transitioning during the rainy seasons, the winds are strong enough to develop wind energy in certain areas. Thunderstorms with gusty winds are a frequent occurrence around Lake Victoria.
Summary
Ariana’s oil and gas infrastructure does not operate at optimal efficiency due to a broad mix of equipment and technology from several foreign countries and a lack of spare parts for some of its Western equipment. The Arianian hydrocarbon industry continues to rely on technology that is over 40 years old and susceptible to mechanical breakdown. While Ariana continues to build new infrastructure mainly in the form of pipelines to transport oil and natural gas around its country, the government spends its money on these new projects while failing to maintain the hydrocarbon infrastructure already in place.
| DATE Africa Quick Links . | |
|---|---|
| Amari | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Kujenga | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Nyumba | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Ziwa | Political • Military • Economic • Social • Information • Infrastructure • Physical Environment • Time |
| Other | Non-State Threat Actors and Conditions • Criminal Activity • DATE Map References • Using The DATE |